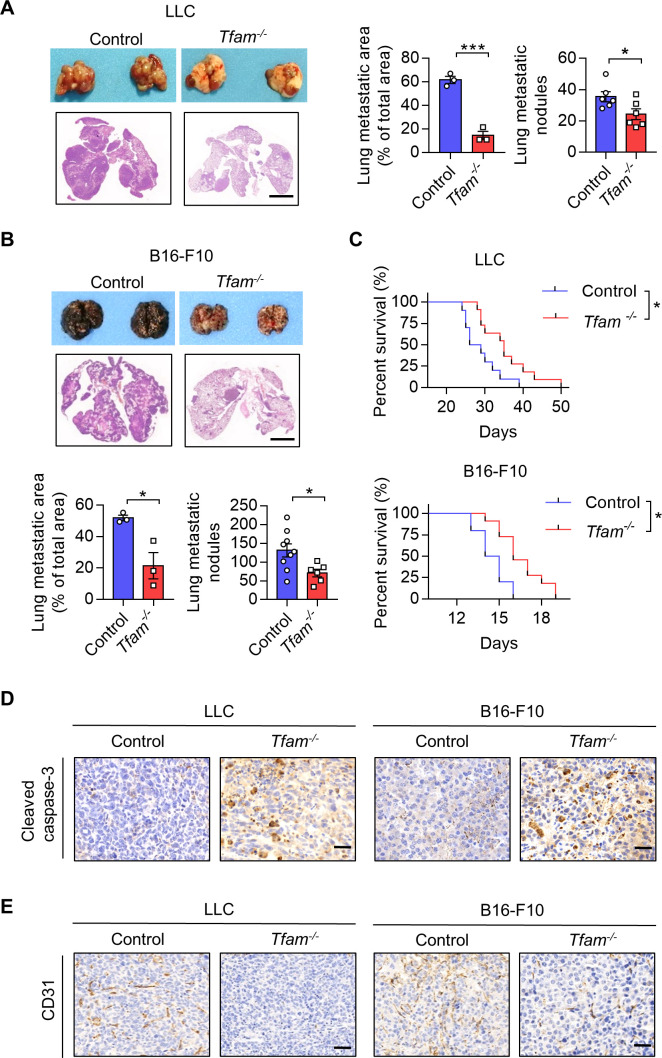
Figure 1.
Low expression of Tfam in myeloid inhibits lung tumor growth. (A, B) Tfam deletion in myeloid inhibited tumor growth in LLC (A) or B16-F10 (B) lung metastatic tumor models. LLC cells (5×105) or B16-F10 cells (2×105) were intravenously injected into control or Tfam-/- mice to establish experimental pulmonary metastasis models (n=6–9 mice), Tfamfl/fl littermates and wild type were used as control. Mice were sacrificed on day 24 (LLC models) or day 14 (B16-F10 models), and pulmonary physiology was evaluated, including gross images and H&E staining of lung, measurement of metastatic area (n=3 mice’s lungs were paraffin embedded) and nodules (n=6–9 mice). Scale bars represent 2 mm. (C) Tfam deletion in myeloid prolonged the survival of tumor-bearing mice. Survival statistics of mice from LLC (5×105) or B16-F10 (5×105) lung metastatic tumor models (n=10–11 mice). (D, E) Immunohistochemical staining of cleaved caspase-3 (D) or CD31 (E) in lungs of the mice described in (A, B). Scale bars represent 20 µm. Data are represented as mean±SEM. Statistical significance in (A, B) was determined by a two-sided unpaired t-test. Survival curve data in (C) were analyzed by log-rank (Mantel-Cox test). Representative results in (A–C) and pictures in (A, B, D, E) from two independent experiments are shown. *p<0.05, ***p<0.001. LLC, Lewis lung carcinoma.