Figure 3.
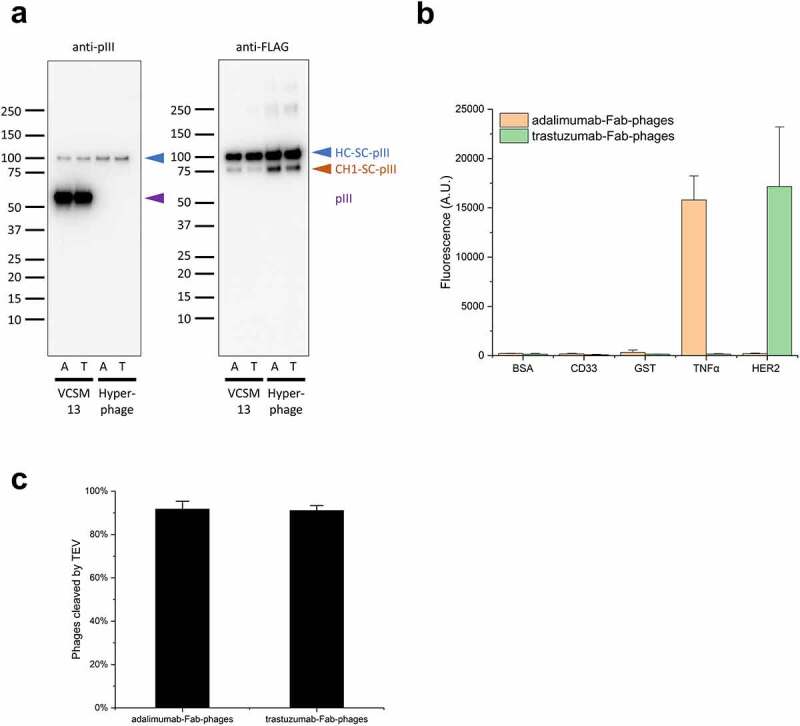
Production of Fab-phages.
(a) Immunoblots of SpyDisplay phages displaying Fabs of adalimumab (A) or trastuzumab (T) and produced with VCSM13 or Hyperphage as helper phage. Detection was performed with anti-M13-pIII followed by sheep anti-mouse IgG (H/L):HRP or anti-FLAG-HRP. Bands corresponding to the heavy chain fusion, degraded heavy chain fusion, and wildtype pIII are marked. (b) ELISA with polyvalent Fab-phages on cognate and irrelevant antigens, detection with anti-pVIII-HRP. (c) Fractions of monovalent Fab-phages eluted from MaxiSorp plates after treatment with TEV Protease for 30 minutes, relative to buffer control.
