Figure 4.
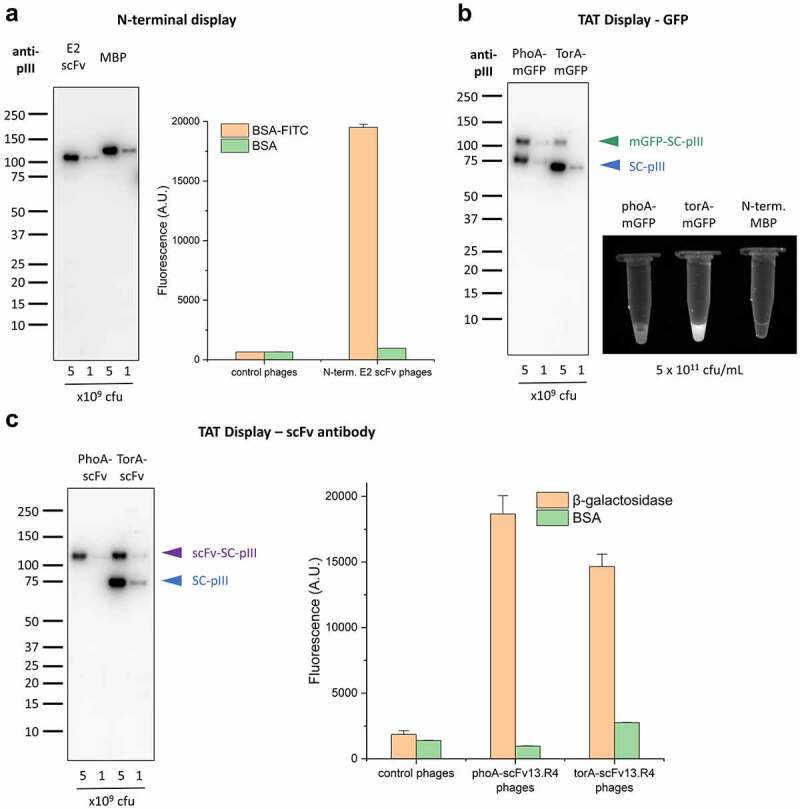
Versatility of display setups with SpyDisplay.
(a) Left: Immunoblot analysis of polyvalent SpyDisplay phages displaying the E2 scFv or MBP with an N-terminal SpyTag. Detection was performed with anti-M13-pIII followed by sheep anti-mouse IgG (H/L):HRP. Right: ELISA of polyvalent phages displaying N-terminally SpyTagged E2 scFv on control (BSA) or cognate antigen (BSA-FITC), in comparison to control phages (displaying N-terminally SpyTagged MBP). (b) Left: Immunoblot analysis of polyvalent SpyDisplay phages displaying mGFP-SpyTag with a PhoA or TorA leader peptide. Detection performed with anti-M13-pIII followed by sheep anti-mouse IgG (H/L):HRP. Right: Fluorescence image of GFP-phages and control phages at equal concentrations (5 × 1011 cfu/mL) in microcentrifuge tubes. (c) Left: Immunoblot analysis of polyvalent SpyDisplay phages displaying scFv13.R4-SpyTag with a PhoA or TorA leader peptide. Detection performed with anti-M13-pIII followed by sheep anti-mouse IgG (H/L):HRP. Right: ELISA of polyvalent phages displaying scFv13.R4 with on control (BSA) or cognate antigen (b-galactosidase), in comparison to control phages.
