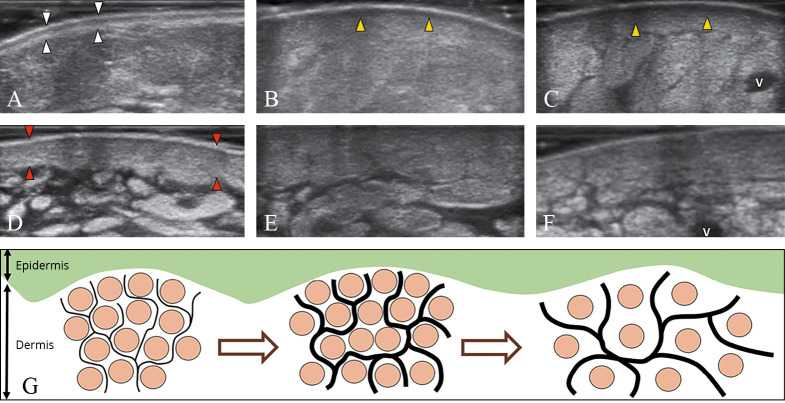
Figure 6.
—The normal trilaminar structure of the dermo-epidermal complex (white arrowheads) (A). This pattern gradually disappears in dermal edema (arrowheads; yellow in the online version), usually starting from the papillary dermis (B) and progressively/also involving the reticular dermis (C). Dermal sclerosis (arrowheads; red in the online version) which is initially characterized by cellular infiltration and thickening (D), can lead to loss of the dermo-hypodermal interface (E) until the end-stage of dermal fibrosis (F). Schematic drawing shows the different phases of dermal backflow with distension of the subepidermal lymphatic plexus (black lines) and rarefaction of the collagen bundles (light grey dots; brown in the online version) of the interstitial space (G). V: vein.