Figure 2.
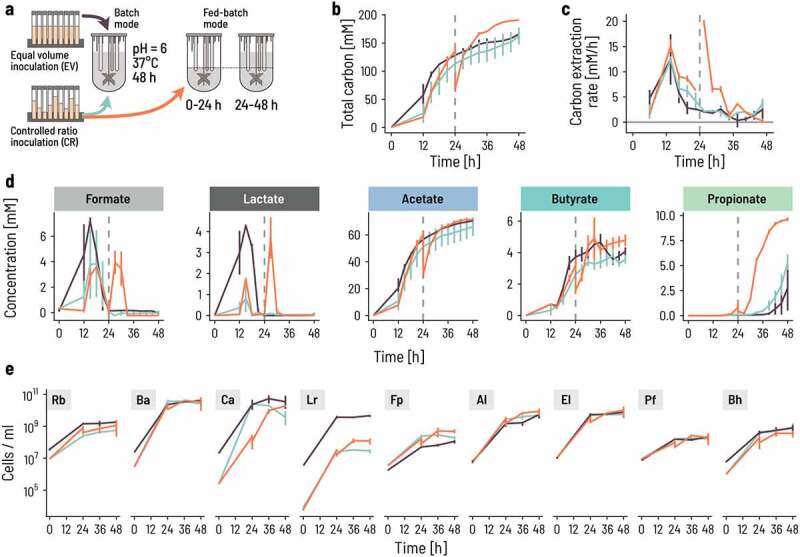
Fed-batch and controlled inoculation ratios of strains promote the successional colonization of bioreactors. a. Two adjustments to the fermentation strategy were compared: using either a batch or a fed-batch setup over 48 h with two different inoculation ratios, ‘equal volumes’ (EV; black lines) or ‘controlled ratio’ (CR+batch, green lines; CR+fed-batch, Orange lines). Batch fermentation was inoculated at 0.33% v/v and fed-batch bioreactors at 0.66% v/v to balance the doubling of medium during fed-batch fermentation. The volume was doubled by adding fresh medium after 24 h in fed-batch mode. b. The total concentration of metabolites produced, expressed in carbon mol concentration, increases steadily in batch mode with either inoculation ratios (EV: black, CR: green). The vertical dashed line indicates the time of medium refill for the fed-batch setup. Each of the three conditions were run in duplicate. Lines and vertical bars show the mean and spread, respectively. Metabolites were quantified by HPLC-RI analysis. Total carbon production was calculated by summing the C-mol of all measured metabolites. c. We computed the rate of carbon extraction as the empirical difference of the C-mol concentration during the last measurement period and expressed per unit time (hour, h). The lines show the mean of, and the vertical segments show the spread between the duplicates. d. Intermediate (formate, lactate) and end (acetate, butyrate, propionate) metabolites are dynamic during the 48 h fermentation. Each line shows the mean of, and the vertical segments the spread between the duplicates. e. The growth of the nine strains differed between the strategies. Cell counts were determined by qPCR, whereby each time point was measured in triplicate. The lines show the median and the vertical segments show the min and max of the triplicate. The measured gene counts are normalized by the 16S rRNA gene copy number of each strain. Rb: R. bromii; Ba: B. adolescentis; Ca: C. aerofaciens; Lr: L. rhamnosus; Fp: F. prausnitzii; Al: A. lactatifermentans; El: E. limosum; Pf: P. faecium; Bh: B. hydrogenotrophica.
