Figure 5.
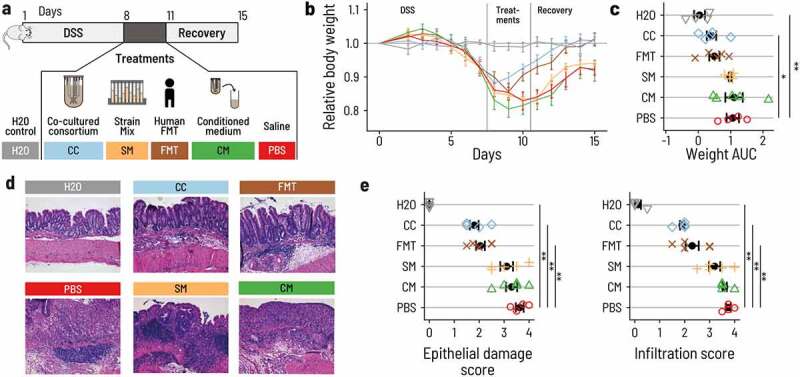
PB002 accelerates recovery after DSS-induced colitis in mice. a. Acute colitis was induced in female C57BL/6 mice by supplementing the drinking water with DSS for 7 d (from day 1 to day 8). At day 8, mice were switched back to normal drinking water. Mice were treated once a day by 200 μL oral gavage on days 8, 9, and 10 with the co-cultured consortium (CC, blue), the non-co-cultivated strain mix (SM, Orange), the conditioned medium from the continuous fermentation (CM, green), or with FMT from a healthy human donor (FMT, brown). The control group was given normal water throughout the whole experiment (H2O, gray), and the DSS control group was gavaged with phosphate-buffered saline (DSS, red). Mice were euthanized at day 16. N = 4 to 5 per group. b. Mice treated with CC or FMT regained body weight more rapidly than mice that received the other treatments. Error bars are the standard errors. c. Area under the curve (AUC) of the daily relative body weight for each mouse. Only CC-treated mice had an AUC that was significantly lower than the DSS control mice (linear model, beta = – 0.65, p = .030). The error bars show the confidence interval for the mean. d. Representative light micrographs of large intestine sections at the time of euthanasia (H&E staining, 10 X magnification). CC and FMT showed structural recovery of the epithelium comparable to the control group. Mice that received CM, SM, or PBS showed a substantial degradation and inflammation of the cecal epithelium. e. Histological assessment of the epithelial damage and infiltration in the distal colon. Treatment with CC and FMT showed reduced epithelial damage and infiltration compared to PBS (linear model, p < 10−4 for all marked comparisons).
