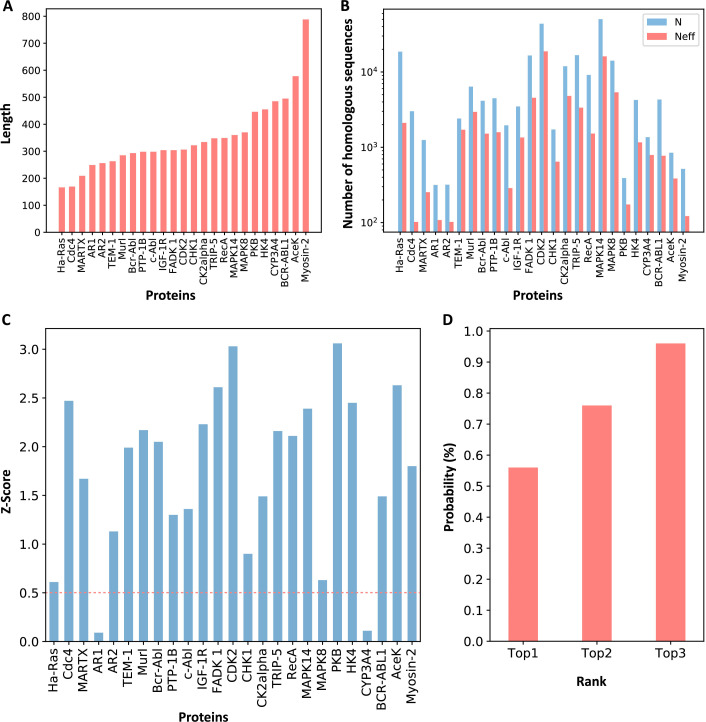
Figure 2. Z-scores of allosteric pockets and probabilities of ranking an allosteric pocket in the top 3.
(A) The sequence lengths of all proteins in our data set. (B) The number of homologous sequences. Neff represents the number of effective homologous sequences obtained under 80% reweighting. (C) Z-scores of allosteric pockets on proteins in the data set. Among the 25 allosteric pockets, the Z-scores of 23 allosteric pockets were greater than 0.5. (D) The probabilities that the known allosteric pockets were ranked in the top 1, top 2, and top 3.