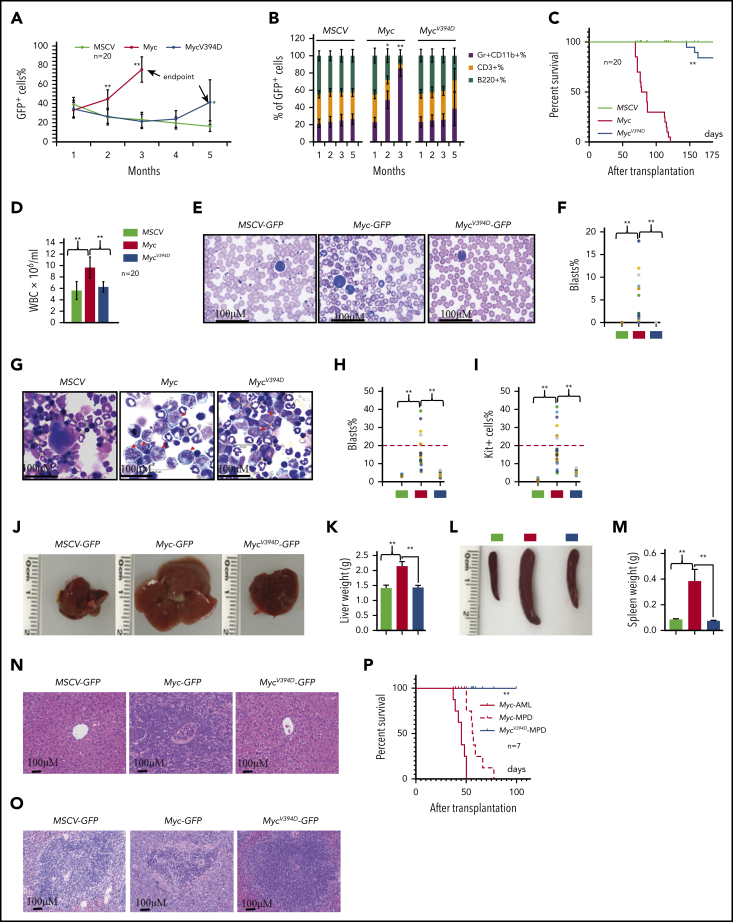
Figure 2.
Reduced leukemogenic capacity of MycV394D-transduced HSPCs compared with Myc-transduced HSPCs. c-Kit+ HSPCs were transduced with MSCV-GFP, Myc-GFP, or MycV394D-GFP, respectively. The transduced HSPCs were purified by FACS 2 days posttransduction and transplanted into lethally-irradiated recipient mice, which were observed for leukemia development. Twenty mice were transplanted for each group. The blood cell engraftments of the transduced HSPCs were analyzed over time by examining the percentage of GFP+ cells in PB of the recipient mice (A). The data for the last time point in both Myc and Mycv394d groups were collected when the mice were euthanized (end point). The lineage commitments of the transduced HSPCs were evaluated by examining the percentages of Gr1+CD11b+ myeloid cells, B220+ B lymphocytes, and CD3+ T lymphocytes within the GFP+ cells (B). Survival of the recipient mice is demonstrated by Kaplan-Meier analysis (C). Leukemia/MPD was verified immediately after the death of the mice by examining the WBCs in PB (D), leukemic blasts in PB (E-F), leukemic blasts in BM (G-I), liver size (J-K), spleen size (L-M), as well as leukemic cell infiltration in livers (N) and spleens (O). *P < .05; **P < .01. (P) BM cells were collected from Myc-AML, Myc-MPD, and MycV394D-MPD mice and transplanted into second-round recipient mice, respectively. Mice were observed for AML or MPD-related death. The survival of the recipient mice is demonstrated by Kaplan-Meier analysis.