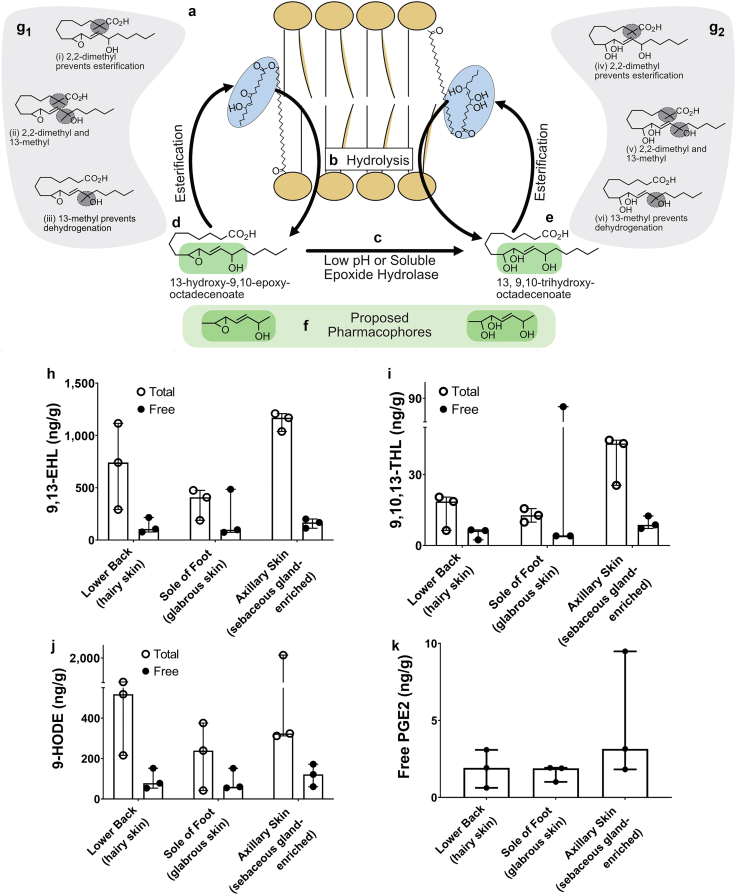
Figure 1.
LA metabolites are found in both the free and total pools of fatty acids in human skin. A box represents the schematic depiction of (a) LA or oxylipins (i.e., 9,13-EHL and 9,10,13-THL) derived from LA, which are esterified into lipid membranes. (b) Hydrolysis by enzymes such as phospholipases can release esterified oxylipins as free acids from the membrane where they can bind to receptors or participate in molecular processes. (c) Epoxide hydrolysis in a low pH environment or by epoxide hydrolases can convert 9,13-EHL to 9,10,13-THL. (d, e) Free acid oxylipins can be esterified into the phospholipid bilayer. (f) Proposed active sites (i.e., pharmacophores) of oxylipins are highlighted. (g) Stable analogs of 9,13-EHL and 9,10,13-THL can be synthesized to prevent esterification and/or prevent degradation of the pharmacophore. Concentrations of oxylipins measured (h) 9,13-EHL, (i) 9,10,13-THL, (j) 9-HODE, and (k) PGE2 in human skin. Data in panels h–k are presented as mean ± SD; no statistical tests were run on these data. Each data point corresponds to one biological replicate. n = 3. 9,10,13-THL, 9,10,13-trihydroxy-octadecenoate; 9,13-EHL, 13-hydroxy-9,10-epoxy octadecenoate; HODE, hydroxyoctadecenoate; LA, linoleic acid; PGE2, prostaglandin E2.