Figure 1. Associations between LVH/biomarker categories and incident ADHF events and mortality.
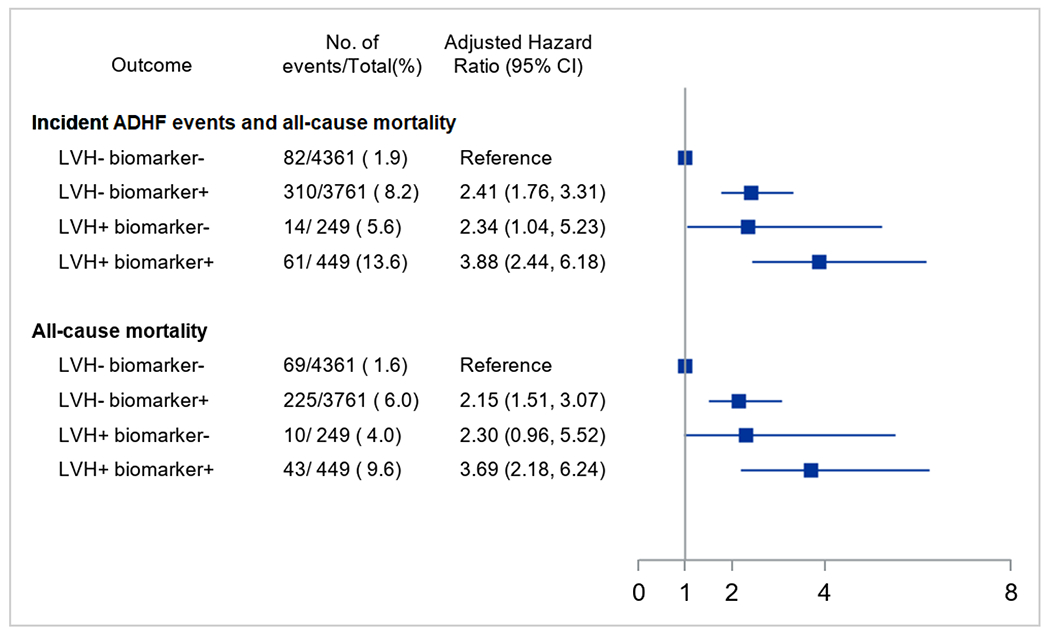
Hazard ratios with 95% confidence intervals obtained from multivariable Cox proportional hazards models that included demographics (age, sex, race, site), treatment assignment, and clinical characteristics (body mass index, smoking status, prevalent CVD, systolic blood pressure, estimated glomerular filtration rate, and low density lipoprotein cholesterol). Combined LVH and biomarker categories include: 1) no LVH and non-elevated cardiac biomarkers (LVH− biomarker−), 2) no LVH and elevated cardiac biomarkers (LVH− biomarker+), 3) LVH and non-elevated cardiac biomarkers (LVH+ biomarker−), and 4) LVH and elevated cardiac biomarkers (LVH+ biomarker+). Elevated cardiac biomarkers defined as hs-cTnT ≥ 14 ng/L or NT-proBNP ≥ 125 pg/mL. Abbreviations: ADHF, acute decompensated heart failure; CVD, cardiovascular disease; HR, hazard ratio; hs-cTnT, high-sensitivity cardiac troponin T; LVH, left ventricular hypertrophy; NT-proBNP, N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide; SPRINT, Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial.
