Figure 5. OxPLs are increased in the lungs of SR-BI−/− mice.
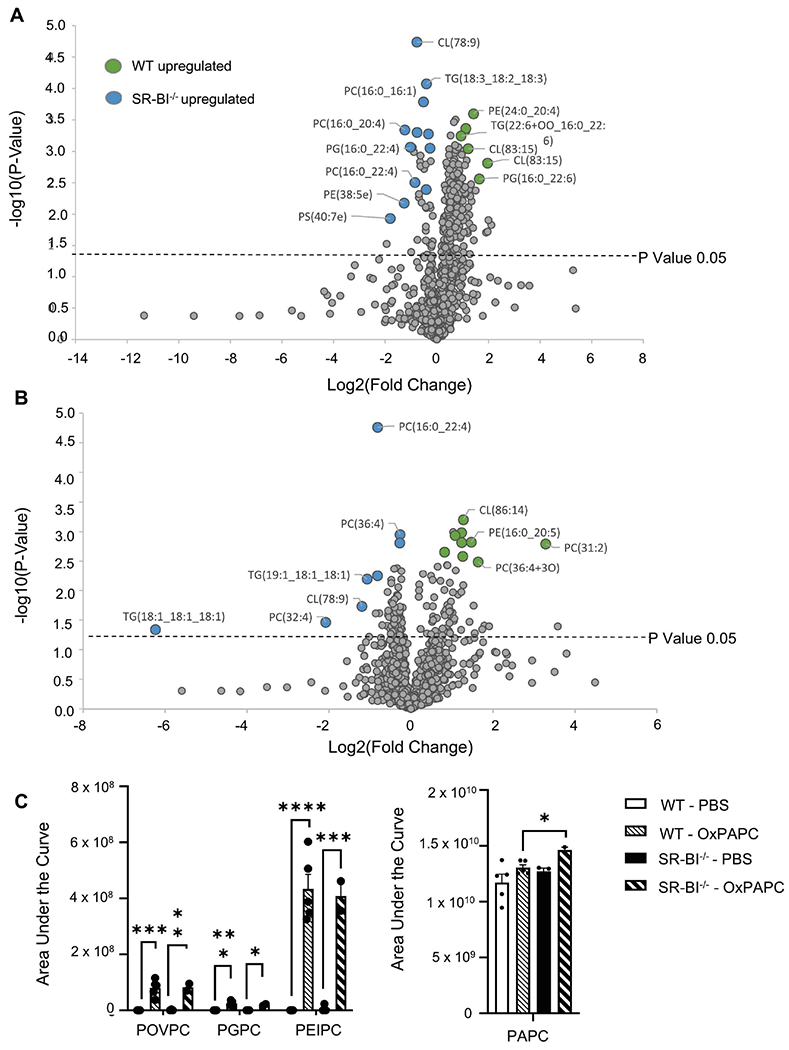
Female WT or SR-BI−/− mice were exposed to PBS or oxPAPC via oropharyngeal (o.p.) aspiration and were euthanized 4 h after exposure. Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) was collected for LC-MS/MS analysis. (A) Relative phospholipid concentrations were compared between WT and SR-BI−/− mice after PBS exposure and (B) after OxPAPC exposure. Increased fold change values for WT animals are shaded green while increased fold change values in SR-BI−/− mice are shaded blue and (C) the area under the curve quantitation of relative concentrations of oxidized lipid species POVPC, PGPC, PEIPC, and PAPC normalized to a deuterated PC internal standard (PC-IS). *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001; n=3-6 per group.
