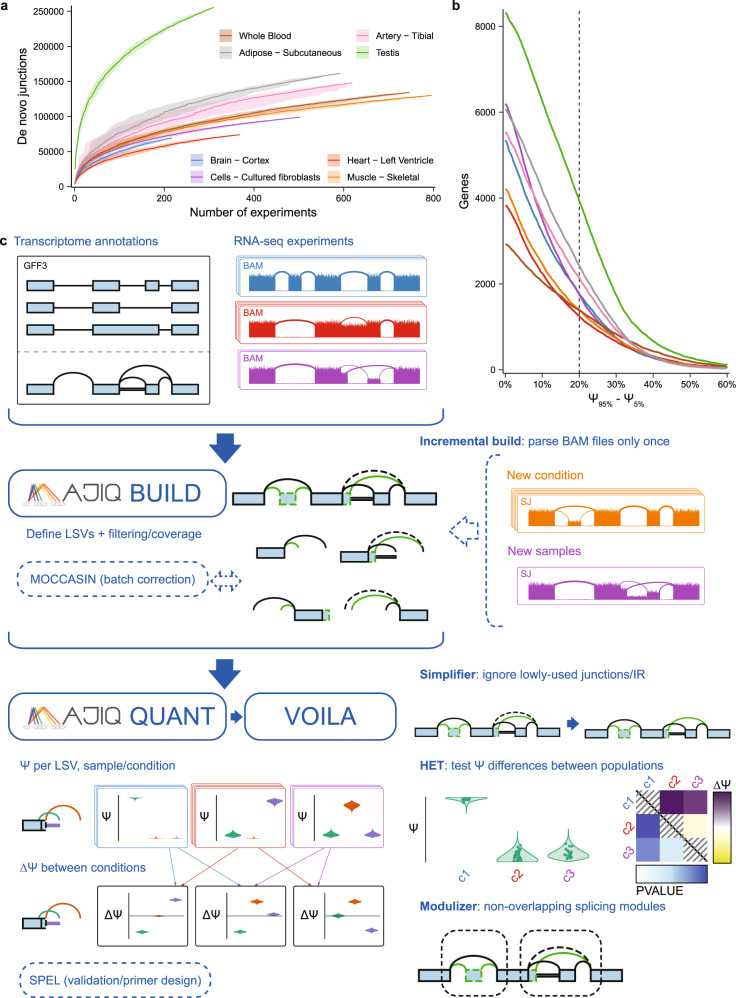
Fig. 1. MAJIQ efficiently and accurately models, quantifies, and visualizes RNA splicing from large and complex RNA-seq datasets.
a The number of identified distinct unannotated de novo junctions increases with larger subsets of different tissues from GTEx. Lines show the median over 30 randomly selected permutations over experiments in each subset, confidence bands show the 5th to 95th percentiles over permutations of samples per tissue. b The number of genes with at least one junction where the difference between the 95th percentile and 5th percentile of PSI exceeds a given value for different tissues from GTEx (same tissues/colors as in a). Dashed vertical line indicates how many genes have a difference in PSI exceeding 20%. c MAJIQ combines annotated transcript databases and coverage from input RNA-seq experiments to build a model of each gene as a collection of exons connected by annotated and de novo junctions and retained introns (splicegraph). Junctions and retained introns sharing the same source or target exon form local splicing variations (LSVs). MAJIQ quantifies the relative inclusion of junctions and retained introns in each LSV in terms of percent spliced in (PSI, Ψ) and provides VOILA to make interactive visualizations of splicing quantifications with respect to each gene’s splicegraph and LSV structures. MAJIQ v2 introduces an incremental build, which allows RNA-seq coverage to be read from BAM files only once to a coverage file (SJ), accelerating subsequent builds with different experiments. MAJIQ v2 introduces a simplifier, which can be used to reduce splicegraph/LSV complexity by ignoring lowly used junctions and retained introns. MAJIQ v2 introduces a new mode for quantification, HET, which compares PSI differences between populations of independent RNA-seq experiments and accounts for variable uncertainty per experiment. MAJIQ v2 introduces the modulizer, which allows performing analysis relative to non-overlapping splicing modules rather than LSVs.