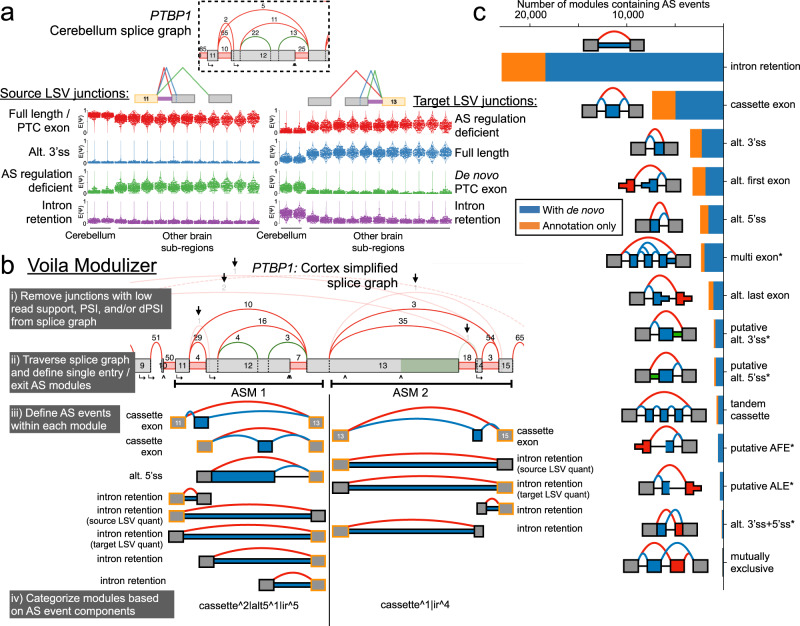
Fig. 4. Downstream analysis of alternative splicing modules with VOILA v2.
a Top shows region of human PTBP1 splicegraph (with reads from combined cerebellum samples) and two LSVs corresponding to a mammalian specific exon skipping event that alters PTBP1 splicing regulatory activity17 (green junction in exon 11 source LSV, left; red junction in exon 13 target LSV, right) and de novo detection of a conserved, PTC-containing exon previously shown to be included in mouse neuronal tissues3 (green junction in exon 13 target LSV). Bottom shows distribution of PSI across the 13 brain tissue groups as well as annotation of each junction. b VOILA Modulizer workflow (gray boxes) and an example region of the PTBP1 splicegraph where junctions that did not meet a median value of 5% or more in any of the 13 brain tissue groups were removed (arrows). Two alternative splicing modules (ASMs) were defined as single entry, single exit regions of the splicegraph and within these modules binary, AS events are defined. Gray exons highlighted in yellow indicate reference exons that belonged to LSVs for which MAJIQ quantification exists. Blue junctions and exonic or intronic regions indicate inclusion of the alternative region of the event and red junctions indicate exclusion of the alternative region. c Stacked bar chart showing the number of binary AS event types that make up AS modules across the 13 brain tissue groups from GTEx. AS event types are represented with a cartoon to the left of the chart and are named to the right of bars. Asterisks indicate non-classical AS event types. Each junction or intron had to have a median of values of 5% or more across the samples of at least one tissue group to contribute to AS module definitions. Blue regions indicate AS events that contained de novo junctions and/or introns not found in the annotated transcripts (Ensembl v94) while orange regions indicate AS events containing only annotated junctions and introns.