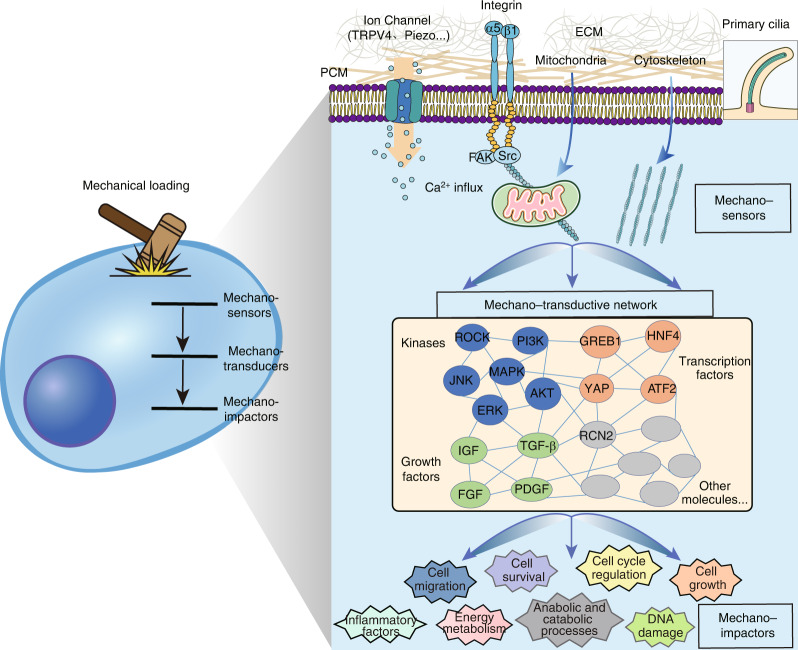
Fig. 1.
The three-tiered cascade of mechanotransduction pathways in cells. The first structures influenced by mechanical stimulation are different types of mechanosensors, including pericellular matrix (PCM) and extracellular matrix (ECM) components, mechanically gated ion channels and porins (such as TRPV4 and Piezo), integrins, mitochondria, cytoskeleton, and primary cilia. Mechanotransducers include multiple types of factors, such as kinases (ROCK, PI3K-AKT, MAPK, etc.), growth factors (IGF, TGF-β, etc.), transcription factors (YAP, GREB1, etc.), secretory proteins (RCN2, etc.), and other molecules, which are activated by mechanosensors and then alter specific downstream molecules. Mechanoimpactors are the final outputs of mechanical stimulation and cause changes in cell phenotypes and behaviors, such as cell migration, survival, growth, energy metabolism, and inflammation