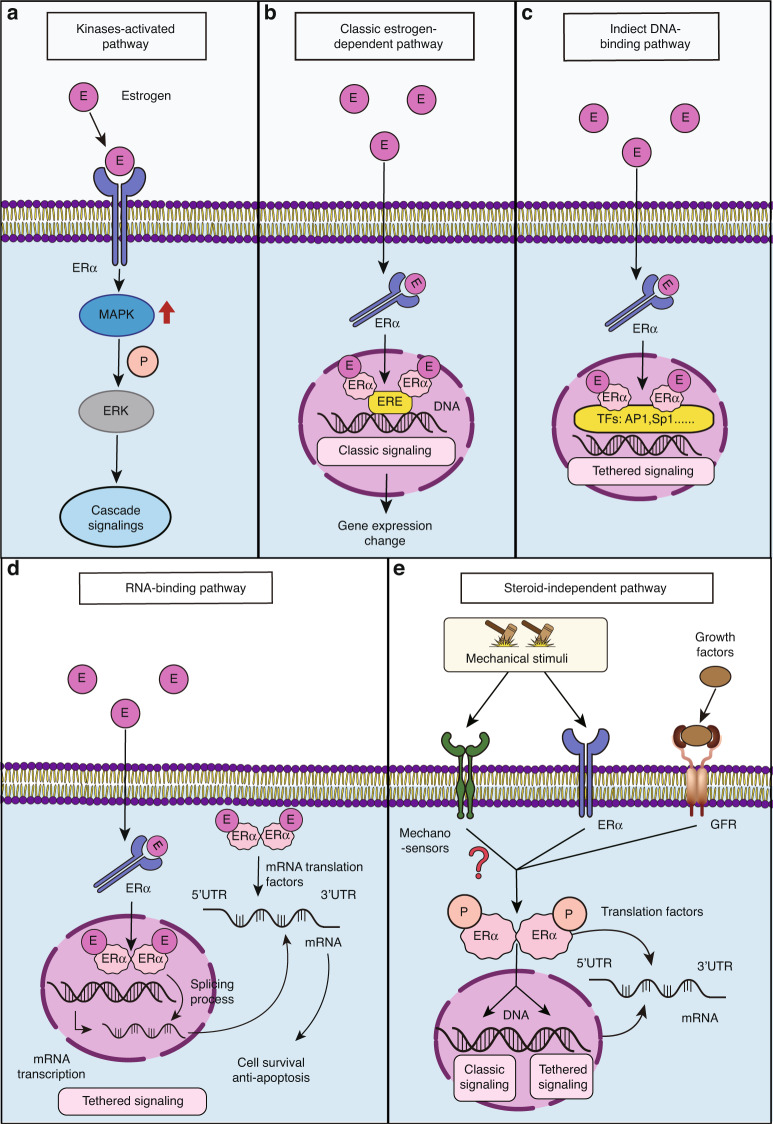
Fig. 4.
Known functions of ERα. a–d Ligand-dependent regulatory pathways. ERα binds with ligands such as E2, which can (a) directly activate MAPK signaling, b bind with DNA to function as a transcription factor (classic signaling factor), c bind with other transcription factors to influence gene expression (tethered signaling), and d modulate mRNA splicing or translational processes by binding to mRNA. e Steroid-independent regulatory pathways. ERα can be activated by mechanical load or several growth factors, E: estrogen, ERα: estrogen receptor α, MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinase, ERK: extracellular signal-regulated kinase, P: phosphorylation, ERE: estrogen response element, TF: transcription factor, AP1: activating protein-1, Sp1: specificity protein 1, and GFR: growth factor receptor