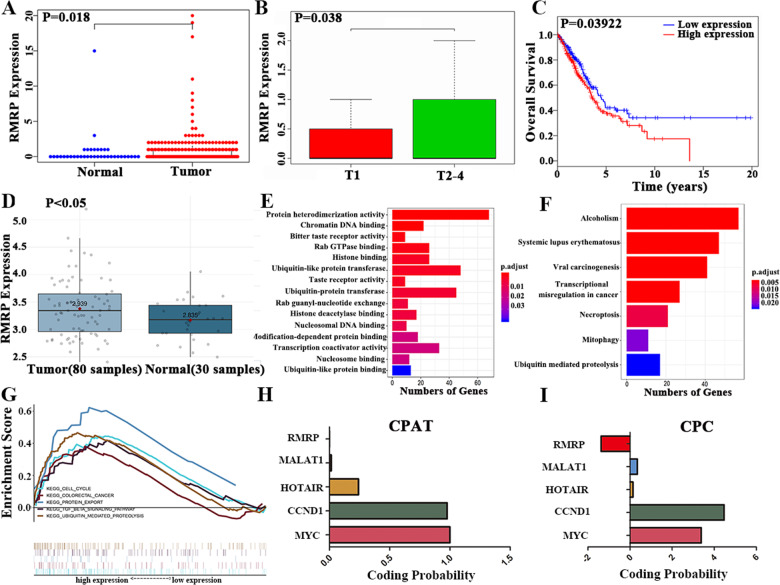
Fig. 1. Integrated analysis of NSCLC reveals that lncRNA-RMRP is a potential biomarker for NSCLC patients.
A. RMRP was significantly upregulated in NSCLC tissues (n = 535) as compared to normal lung tissues (n = 59) (Wilcoxon signed-rank test). B. RMRP was associated with tumor size in NSCLC patients (n = 335; Wilcoxon signed-rank test). C High RMRP expression was associated with worse survival rates by Kaplan–Meier method (n = 504). D RMRP was upregulated in NSCLC tissues (n = 80) compared to normal lung tissues (n = 30) in GSE43458, as shown in the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database, which was analyzed by the online tool Lung Cancer Explorer (https://lce.biohpc.swmed.edu/lungcancer/). E Gene Ontology (GO) results showed that RMRP functions in protein heterodimerization activity, chromatin DNA binding, bitter taste receptor activity, Rab GTPase binding, histone binding, ubiquitin-like protein transferase activity, taste receptor activity, ubiquitin-protein transferase activity, Rab guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity, histone deacetylase binding, nucleosomal DNA binding, modification-dependent protein binding, transcription coactivator activity, nucleosome binding, and ubiquitin-like protein binding. F The KEGG results showed that RMRP was enriched in pathways of Alcoholism, Systemic lupus erythematosus, viral carcinogenesis, transcriptional misregulation in cancer, Necroptosis, Mitophagy—animal and Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis. G The GSEA research showed RMRP was enriched in the cell cycle, colorectal cancer, protein export, TGFB pathway, and ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis pathway. H The protein-coding potential of RMRP through the CPAT database. I The protein-coding potential of RMRP through the CPC database. LncRNA-MALAT1, LncRNA-HOTAIR, CCND1, and MYC were also explored as control.