Fig. 4.
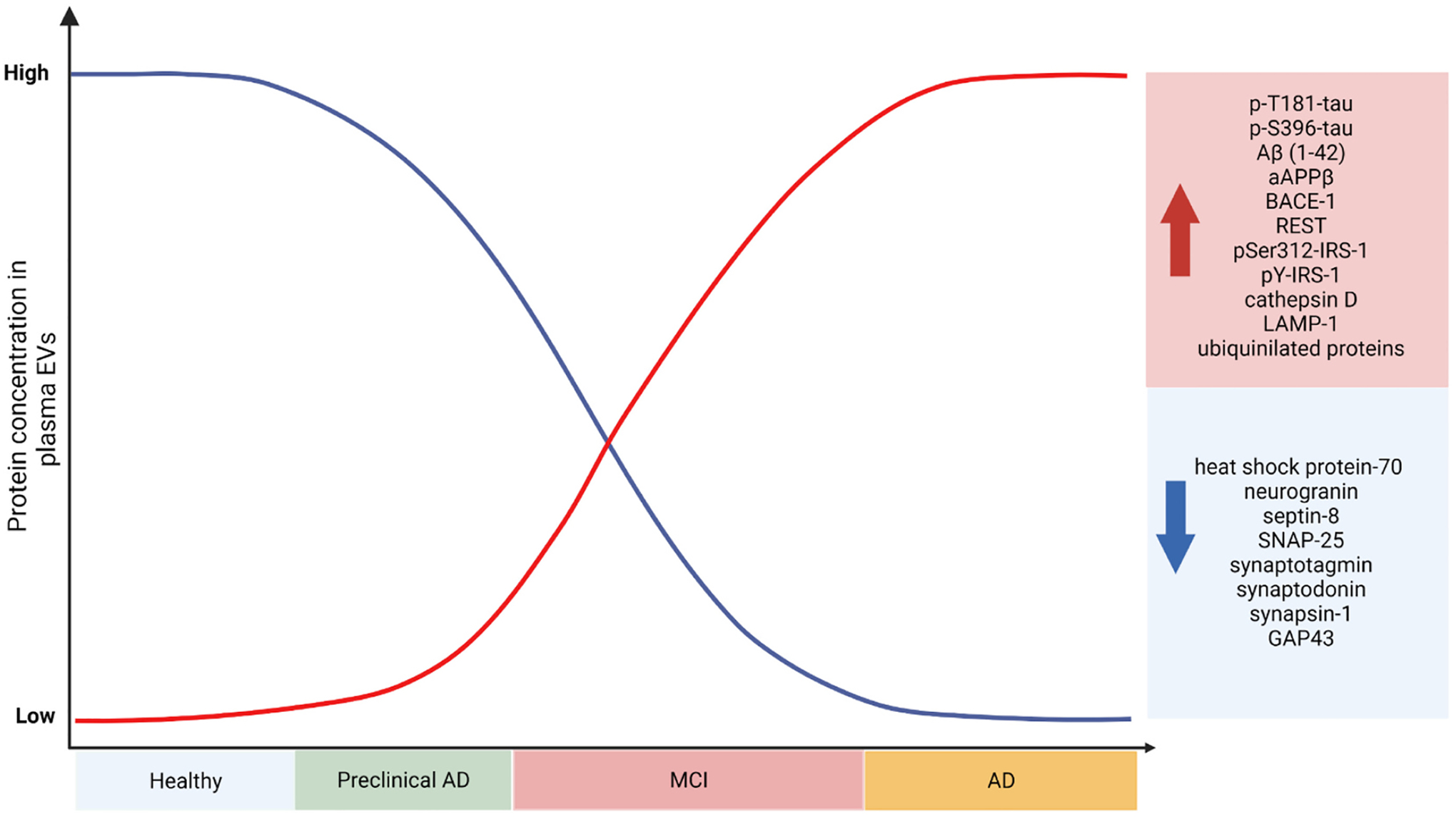
EVs proteins in AD diagnostics. Retrospective and cross-sectional studies of human cohorts have revealed the potential of EV contents as diagnostic and prognostic tools. While the AD biomarker potential of miRNA in EVs has recently started to be investigated, EV protein content has been assessed under multiple clinical conditions and tasks, including their diagnostic and prognostic potential. Based on previous clinical studies (see also Table 2), one group of EVs proteins was detected to be increased as dementia progresses (e.g., total Tau, specific Tau phospho-epitopes, Aβ, ubiquitinylated proteins) while another group of EVs proteins, mostly synapse-related proteins, are found to be decreased in AD. Further longitudinal studies of large and polycentric cohorts of healthy and AD patients are necessary in order to clarify the protein and miRNA cargo of EVs along the progress of AD and identify specific target or groups of targets of protein and/or miRNA EVs cargo with high biomarker value for AD.
