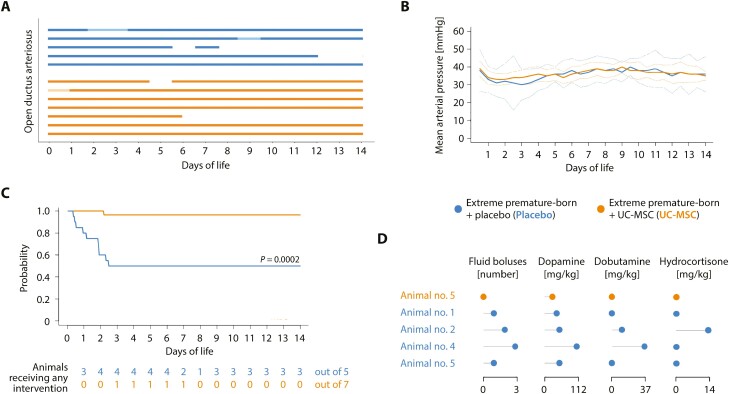
Figure 3.
Umbilical cord tissue-derived mesenchymal stromal cells benefit cardiovascular stability in critically ill, extremely premature-born baboons. (A) Presence of an open ductus arteriosus, assessed by daily echocardiography. Every bar represents an animal; solid lines an open, gaps a closed ductus arteriosus. Opaque parts indicate days where the ductus was not assessable by echocardiography. All observed shunting occurred from the systemic into the pulmonal circulation (left-to-right). No significant differences between groups, comparing data for every 24-hour interval. (B) Temporal progression of the mean arterial pressure, depicted as group mean (solid curves) with 95% confidence interval of the mean (CI95%; dotted curves). No significant differences between groups, comparing data for every twelve-hour interval. (C) Event probability for continuing the experiment without requiring escalating interventions (normal saline bolus, dopamine, dobutamine, hydrocortisone) to maintain mean arterial blood pressures ≥ 25 mmHg. Only the start of a new intervention was defined as event; event frequencies were compared on day of life 14. (D) Cumulative doses of medications in animals requiring interventions for cardiovascular insufficiency. Every row in the lollipop chart represents one animal. See Supplementary Fig. S3 for further information on the volume status of the animals. All data derives from five placebo and seven MSC-treated animals. Statistics: Event frequencies in (A) and (C) were compared using Fisher’s exact method. Welch’s two-sided, unequal variance t-test followed by multiple testing adjustment using Šidák’s correction was used to compare data presented in (B).