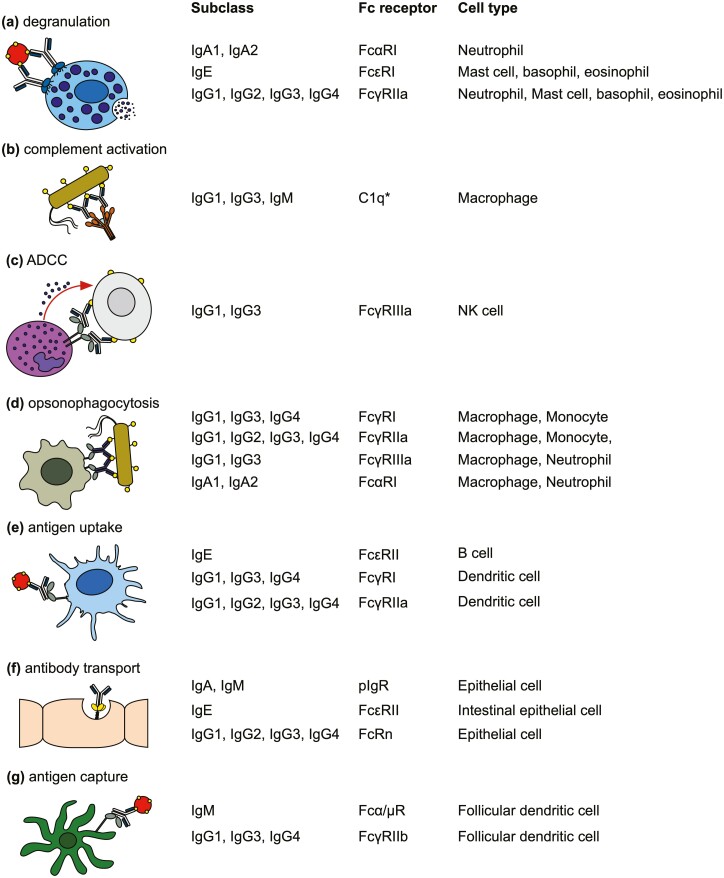
Figure 2:
Fc-dependent antibody functions. Antibodies mediate a variety of effector functions via Fc-dependent interaction with receptors and proteins localised at different sites throughout the body. The most common functions are illustrated here, including (a) degranulation of innate myeloid cells, (b) complement-dependent activation resulting in direct pathogen lysis or enhanced phagocytosis, (c) antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity by NK cells, (d) opsonisation of pathogens to facilitate phagocytosis, (e) facilitated antigen uptake by antigen presenting cells, (f) receptor-mediated transport of antibody across mucosal barriers, and (g) capture of antigen for regulation of germinal centre responses. *C1q is not a receptor but can bind to antibody Fc and cross-link complement receptors on the surface of macrophages, thereby promoting complement-mediated phagocytosis.