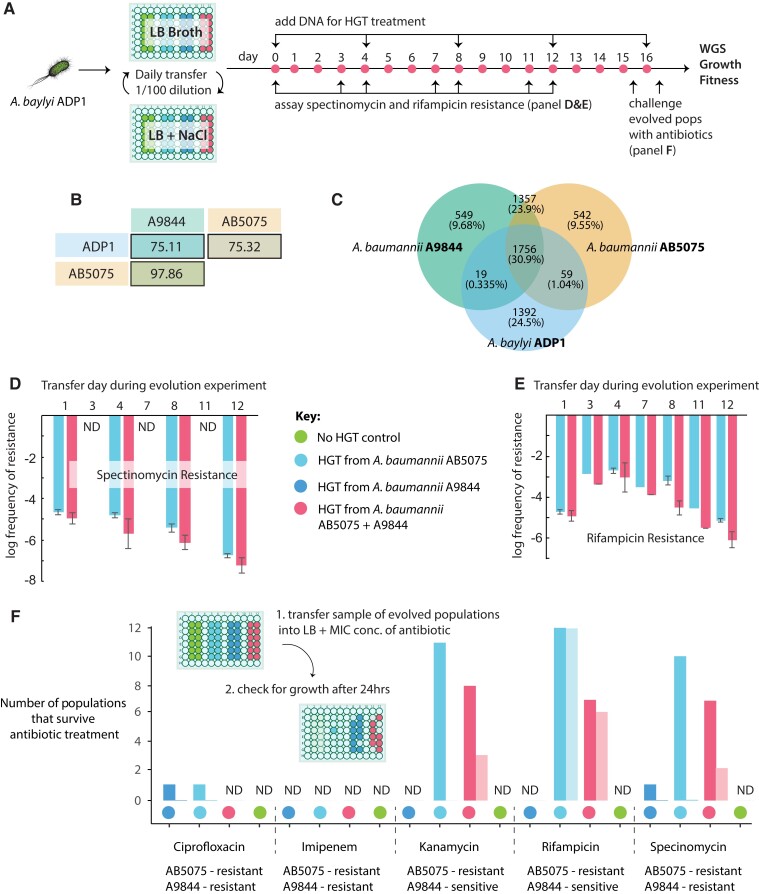
Fig. 1.
(A) Experimental overview. Replicate populations of A. baylyi ADP1 were propagated in LB media alternating between 2% and 4% NaCl. HGT treatment populations were supplemented with gDNA from donor strains of A. baumannii at the beginning of the experiment and at regular intervals. Accurate well positions are shown on the microwell schematic. (B) The average nucleotide identity (ANI) for core genes shared between pairs of genomes used in this study. (C) The proportion of shared and unique genes for the donor (A9844 and AB5075) and recipient (ADP1) genomes, where orthologs sharing 95% amino acid identity are considered shared genes. The average frequency of spectinomycin (D) and rifampicin (E)-resistant colonies across all 12 replicate populations from the AB5075 and mixed HGT treatments. (F) The number of evolved populations that could survive challenge with MIC concentrations of ciprofloxacin, imipenem, kanamycin, rifampicin, or spectinomycin antibiotics. Evolved populations were challenged twice: First, at day 15, after a portion of the culture had been taken to inoculate the day 16 cultures (light-colored bars). Second, at day 16, after the HGT treatment (darker colored bars). The light-colored bars show the number of replicates surviving antibiotic treatment 3 days after the day 12 HGT treatment, while the darker colored bars show the number of replicates surviving antibiotic treatment immediately after the day 16 HGT treatment.