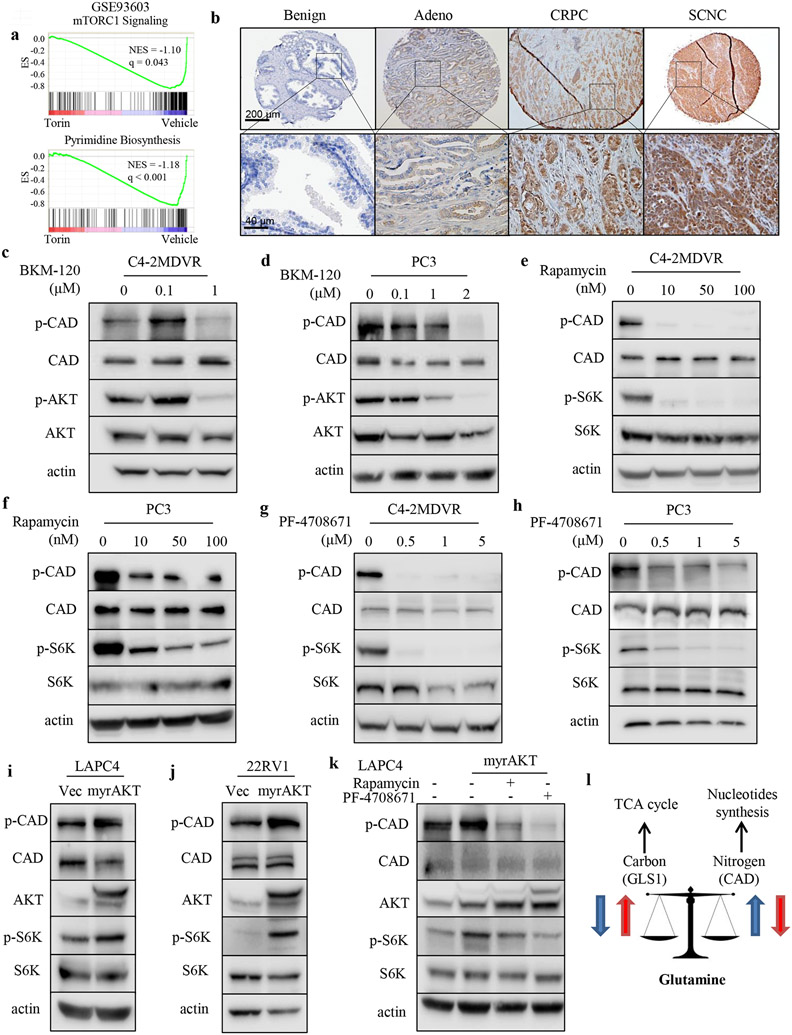
Figure 7.
PI3K-AKT signaling phosphorylates CAD in advanced PCa. A, GSEA of “mTORC1 Signaling” and “Pyrimidine Biosynthesis” gene sets in the comparison of cells treated with torin or vehicle. B, Representative images of phosphorylated CADS1859 IHC staining on the TMAs including benign prostate tissue (n = 40), primary prostate adenocarcinoma (n = 40), CRPC (n = 16) and SCNC (n = 17). Adeno, adenocarcinoma. CRPC, castration-resistant prostate cancer. SCNC, small neuroendocrine prostate cancer. Scale bars are shown as indicated. C and D, Western blot assessment of phosphorylated CADS1859, total CAD, phosphorylated AKTS473 and total AKT protein levels after treatment with the PI3K inhibitor BKM-120 for 48 hours in C4-2MDVR (C) and PC3 (D) cells. E and F, Western blot assessment of phosphorylated CADS1859, total CAD, phosphorylated S6KT389 and total S6 protein levels after treatment with the mTOR inhibitor rapamycin for 48 hours in C4-2MDVR (E) and PC3 (F) cells. G and H, Western blot assessment of phosphorylated CADS1859, total CAD, phosphorylated S6KT389 and total S6 protein levels after treatment with the S6K inhibitor PF-4708671 for 48 hours in C4-2MDVR (G) and PC3 (H) cells. I and J, Western blot assessment of phosphorylated CADS1859, total CAD, total AKT, phosphorylated S6KT389 and total S6 protein levels after infection of myristoylated AKT in LAPC4 (I) and 22RV1 (J) cells. K, Western blot assessment of phosphorylated CADS1859, total CAD, total AKT, phosphorylated S6KT389 and total S6 protein levels after infection of myristoylated AKT together with the PI3K inhibitor (BKM-120) or the mTOR inhibitor (rapamycin) treatment in LAPC4 cells. L, Diagram of proposed mechanism for the crosstalk within glutamine metabolic network.