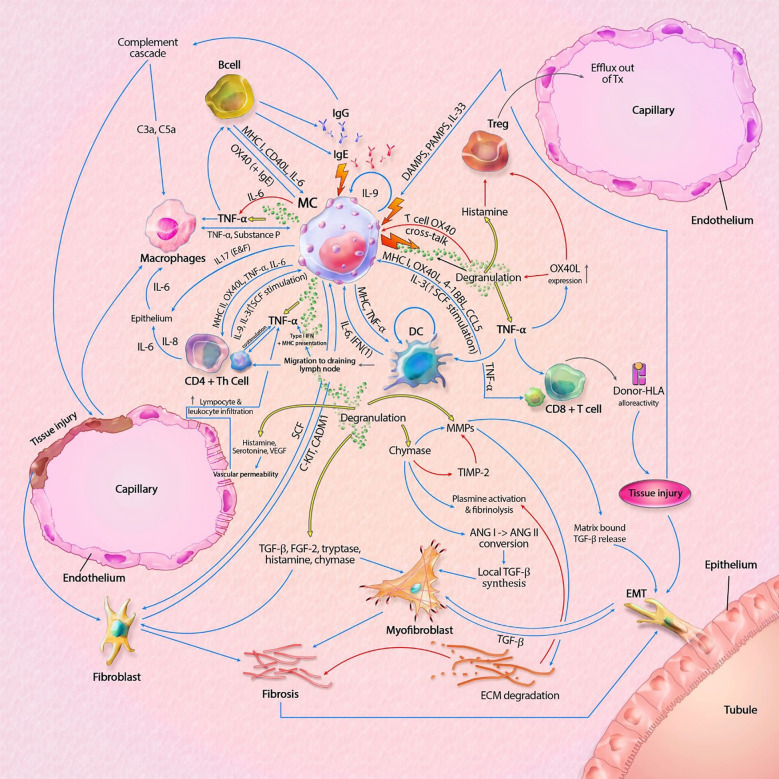
Figure 2.
Mast cell (MC) interactions within the graft during rejection. Pathways can include both cytokines (like TNF-α) and membrane bound interaction (like MHC I-TLR interaction). MC-T cell interaction through OX40L-OX40 cross-linking inhibits MC degranulation, represented by the inhibitory pathway towards degranulation. Innate immune cells can also result in tissue injury, which is not shown in this model. Interaction between APCs, T cells and B cells, resulting in antigen production is also not shown in this model. The model shows almost no inhibitory pathways, explaining the progressive state of fibrosis within KTx even when immunosuppressive drugs are taken. Detailed description of the model can be found within the text. ANG, angiotensin; C3a/C5a, complement component; ECM, extracellular matrix; EMT, epithelial-mesenchymal transition; FGF-2; fibroblast growth factor-2; Ig, immunoglobulin; IL, interleukin; MHC, major histocompatibility complex; MMPs, matrix metalloproteinase; SCF, stem cell factor; tDC, tolerogenic dendritic cell; TGF-β, tissue growth factor beta; Th cell, T helper cell; TIMP-2, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2; TNF-α, tissue necrotic factor alpha; Treg, regulatory T cell (natural); VEGF, Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor. Blue lines symbolize activating pathways, red lines inhibitory pathways, yellow lines represent pre-formed mediators within MCs. Grey lines represent subsequent events. Lighting icons are used in the most profound activation patterns.