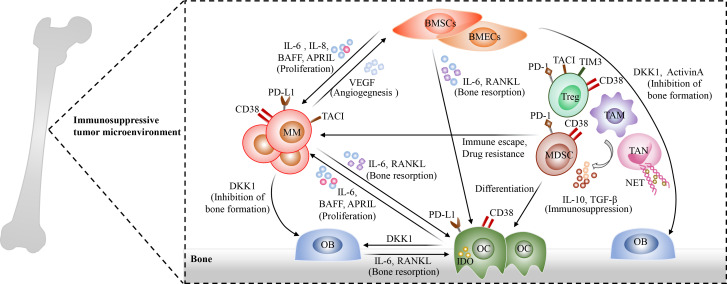
Figure 2.
The complexity of bone marrow microenvironment in MM. Multiple immunosuppressive cells are accumulated in bone marrow microenvironment and exhibit tumor supportive properties, including osteoclasts (OCs)such as osteoclasts (OCs), myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), regulatory T cells (Tregs), regulatory B cells(Bregs), tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs), tumor-associated neutrophils (TANs), and bone marrow stromal cells (BMSCs). These cells interact with surrounding MM cells through direct cell-to-cell contact or producing soluble factors, and then promote the proliferation, immune escape of MM cells as well as Drug resistance. Osteoclasts (OCs) are remarkably increased in the bone marrow microenvironment of MM patients and involved in the occurrence and development of myeloma bone disease. In addition, they produce APRIL, BAFF and IL-6 to promote MM cell proliferation and survival. Meanwhile, OCs act as antigen-presenting cells (APCs) in the bone marrow and exhibit immunosuppressive properties through up-regulating the expression of immune checkpoint molecules, such as PD-L1, CD38 and galectin 9. In turn, MM cells could promote bone resorption activity of OCs through the secretion of IL-6 and RANKL. Immunosuppressive Tregs and MDSCs, which express several immune inhibitory molecules, such as PD1, TIM3, and CD38, are significantly increased in MM bone marrow microenvironment and secrete TGF-β and IL-10 to promote the evasion of MM cells from immune surveillance. TAMs apparently infiltrate the bone marrow, and they promote angiogenesis and induce immune escape and drug resistance of MM cells. In addition, TANs also play an immunosuppressive role in MM bone marrow microenvironment through the release of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs), which could contribute to tumor-associated thrombosis and tumor metastasis. Moreover, BMSCs show an inflammatory phenotype in MM microenvironment. On the one hand, they secrete several cytokines, such as APRIL, BAFF, IL-6, and RANKL; On the other hand, they induce the expression of anti-apoptotic proteins in MM cells, eventually promoting MM cell proliferation and drug resistance. Additionally, plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs), NK cells, and NKT cells exhibit the decreased anti-myeloma activities in bone marrow microenvironment.