Figure 7. STUB1‐mediated degradation of METTL14 has potential clinical relevance.
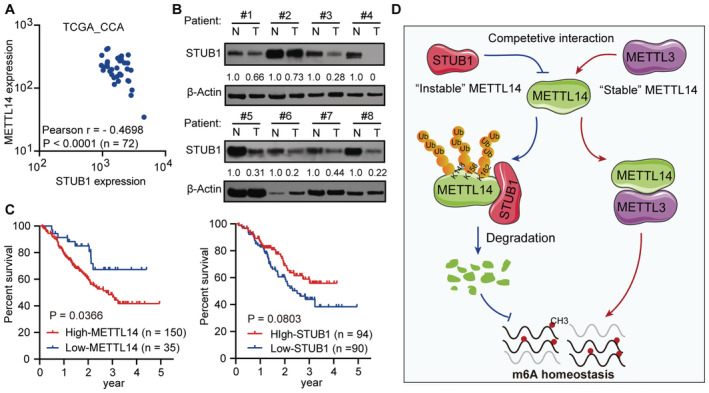
- METTL14 and STUB1 expression show a strong negative correlation in the TGCA data sets consisting of 72 CCA patient samples (Pearson coefficient: −0.4698, P < 0.001).
- Immunoblot analysis showing STUB1 protein levels in eight pairs of CCA patient samples. N, adjacent non‐tumor tissue; T, tumor tissue. β‐actin was used as the loading control. The STUB1/β‐actin densitometric ratio was recorded by ImageJ.
- The 5‐year disease‐free survival of patients with high expression levels of METTL14 (P = 0.0366) and low expression levels of STUB1 (P = 0.0803) in the Fudan University intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (FU‐iCCA) cohort among patient samples within the 5–95% ranges of STUB1 and METTL14 protein levels.
- Working model for the role of the competitive interaction of METTL3 and STUB1 in maintaining METTL14 levels and the subsequent regulation of m6A homeostasis.
Source data are available online for this figure.
