Fig. 5 |. iScore associates with distinct subsets of human AML.
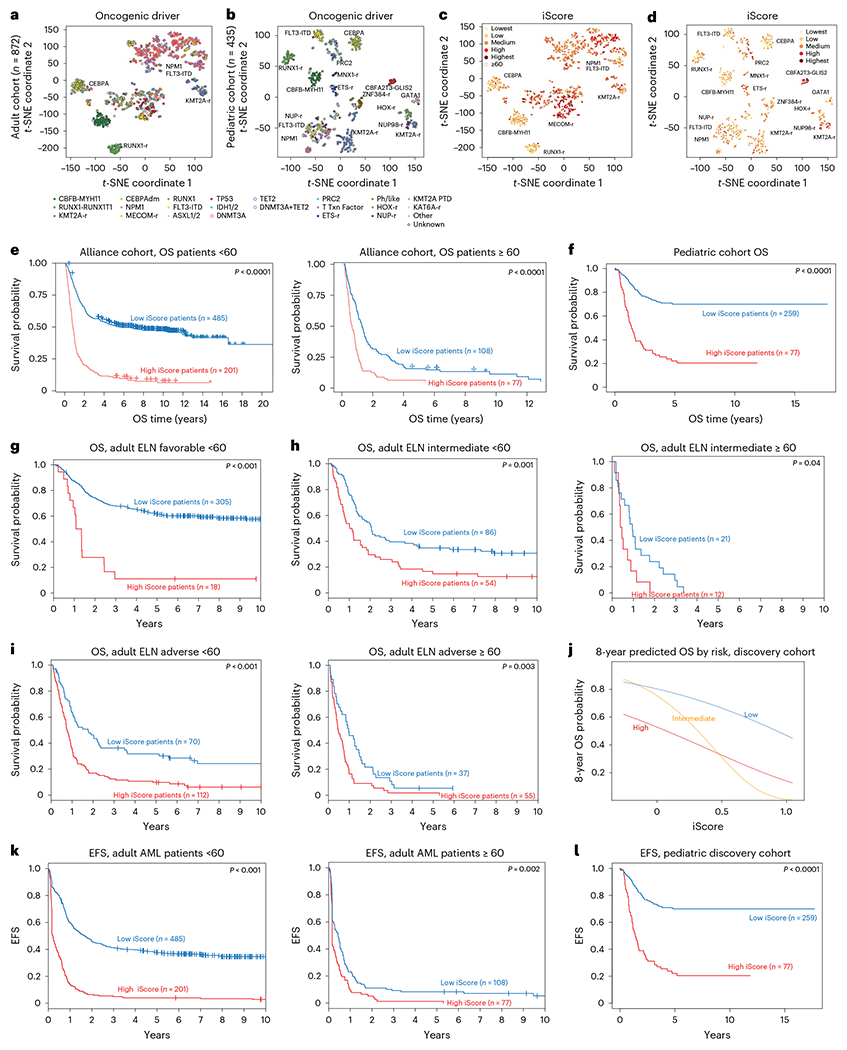
a, t-SNE representation of bulk RNA-seq data of adult patients with AML in the Alliance cohort (n = 872). b, t-SNE representation of bulk RNA-seq data of pediatric patients with AML in a large bulk RNA-seq cohort46 (n = 435). c, Adult iScore in bulk RNA-seq data of patients in the Alliance cohort (n = 872). d, Pediatric iScore in bulk RNA-seq data of patients in a pediatric bulk RNA-seq cohort (n = 435). e, OS of high and low iScore adult patients with AML in the Alliance cohort (n = 872). Log-rank test was used to evaluate significance. f, OS of high and low iScore pediatric patients with AML in the TARGET-AML cohort (n = 336). Log-rank test was used to evaluate significance. g, OS of adult ELN favorable high and low iScore patients in the Alliance cohort (n = 323). Log-rank test was used to evaluate significance. h, OS of adult ELN intermediate high and low iScore patients in the Alliance cohort (n = 140, <60 years old; n = 33, ≥60 years old). Log-rank test was used to evaluate significance. i, OS of adult ELN adverse high and low iScore patients in the Alliance cohort (n = 182, <60 years old; n = 92, ≥60 years old). Log-rank test was used to evaluate significance. j, Eight-year predicted OS in low-, intermediate- and high-risk patients in a pediatric cohort (n = 336). k, EFS in high and low iScore patients in the Alliance AML cohort (n = 686, <60 years old; n = 185, ≥60 years old). Log-rank test was used to evaluate significance. l, EFS in high and low iScore pediatric patients (n = 336). Log-rank test was used to evaluate significance.
