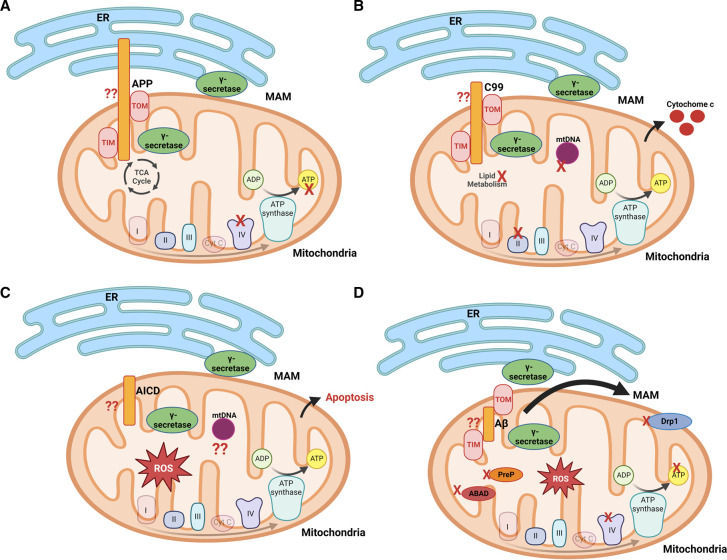
Figure 2. APP, APP fragments, and mitochondria.
Current knowledge and knowledge gaps. (A) Full-length APP and mitochondria. It is unknown if APP translocates into the mitochondria from the ER through MAMs. It is also unknown if APP modulates MAM function. Studies suggest APP inhibits COX (complex IV) and ATP production. Some studies suggest APP associates with TOM and TIM. These findings have not been directly confirmed. Its also unclear the role of full-length APP versus APP fragments. (B) CTF of APP (C99) and mitochondria. It is unknown if C99 translocates into the mitochondria or is generated within mitochondria. Studies suggest C99 inhibits complex II, lipid metabolism, damages mtDNA, and induces cytochrome c release. The role of C99 has not been confirmed as independent from Aβ. (C) AICD and mitochondria. It is unknown if AICD translocates into the mitochondria or is generated within mitochondria. Studies suggest AICD induces ROS and apoptosis when it is localized to mitochondria. Its unknown how it affects mtDNA or transcription of mitochondrial genes. (D) Aβ and mitochondria. It is unknown if Aβ translocates into the mitochondria, is generated within mitochondria, or both. Studies suggest Aβ inhibits COX, ATP production, PreP, ABAD, Drp1, induces ROS, and increases MAM content. Created using Biorender.