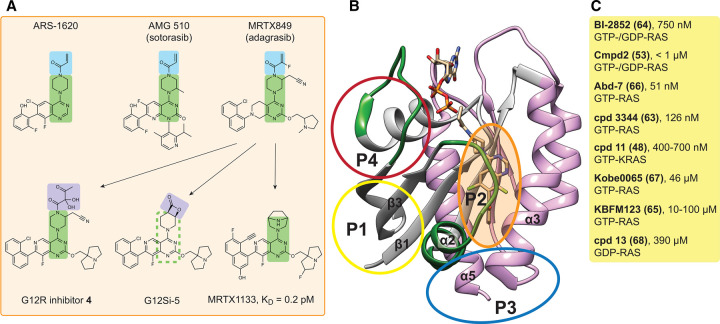
Figure 1. Overview of small molecule inhibitors targeting RAS.
(A) Selected SII-P small molecule inhibitors based on the 4-piperazin-1-yl-pyrimidine scaffold (green highlights). The common acrylamide warhead of KRAS-G12C inhibitors (top row) is highlighted in blue. Adagrasib served as a starting point for additional inhibitors (arrows), including covalent G12R- and G12S-inhibitors, with an α,β-diketoamide warhead or a strained β-lactone electrophile, respectively (purple). Note that the exact stereochemistry of displayed inhibitors has been largely omitted. (B) Crystal structure of GDP-KRAS-G12C in complex with ARS-1620 (PDB ID 5V9U). The RAS structure can be divided into the N-terminal effector lobe (grey), with the switch I and switch II regions labelled in green, and the allosteric lobe (pink). The allosteric binding sites P1–4 are indicated with circles. (C) Current experimental small molecule inhibitors (here those with an affinity <500 µM) target predominantly P1. The RAS affinity and selectivity is indicated for each compound (cpd). References are in brackets after the names [48,53,63–68]. The full list of small molecule inhibitors is contained in Supplementary File S1.