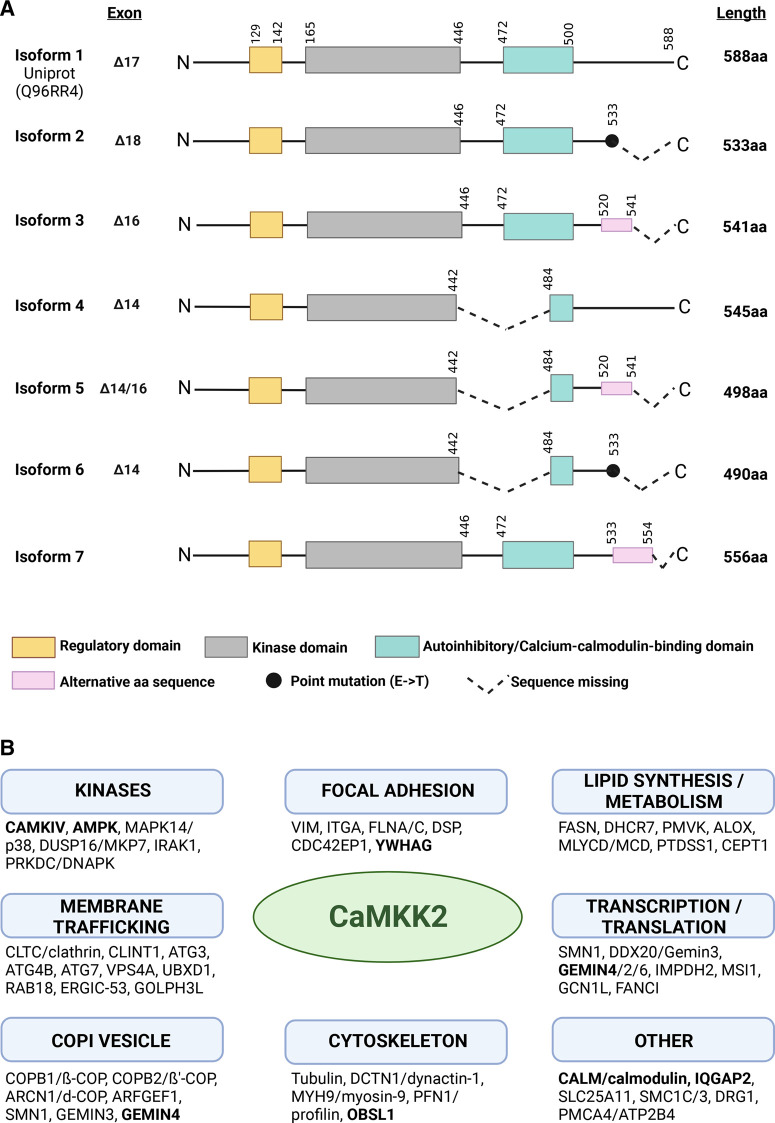
Figure 1. Summary of CaMKK2 domain structure and interactors identified by affinity capture mass spectrometry.
(A) CaMKK2 contains three domains: the regulatory domain, the central serine/threonine kinase domain and the N-terminal autoinhibitory and calcium/calmodulin-binding domain (AID/CBD). There are seven distinct isoforms of CaMKK2 that differ in the C-terminal region due to the splicing of exons. Isoforms 4, 5 and 6 lack exon 14, which encodes the sequence within the AID/CBD that is phosphorylated and facilitates kinase activation. This loss removes the catalytic activity of isoforms 4, 5 and 6 and these, therefore, are found to be inactive. Isoforms 2 and 6 have truncated C-termini that may affect the inherent kinase activity. Furthermore, exon 17 is absent from isoform 1 and exon 18 is absent from isoform 2. Isoforms 3 and 5 have a deletion of exon 16 resulting in a change in the open reading frame, producing an alternative sequence (KPTRECESLSELKEARQRRQPP) from the original isoform 1 sequence (QGSEDNLQGTDPPPVGEEEVLL) and an early termination of the transcript [13]. Isoform 3 is the predominant form of CaMKK2 expressed in prostate cancer [95]. (B) A summary of interaction partners of CaMKK2 that have been identified by affinity capture mass spectrometry is displayed in functional categories which illustrate the range of interactions associated with CaMKK2. Protein interactions that have been validated by independent biochemical experiments are displayed in bold. Figure created with BioRender.com.