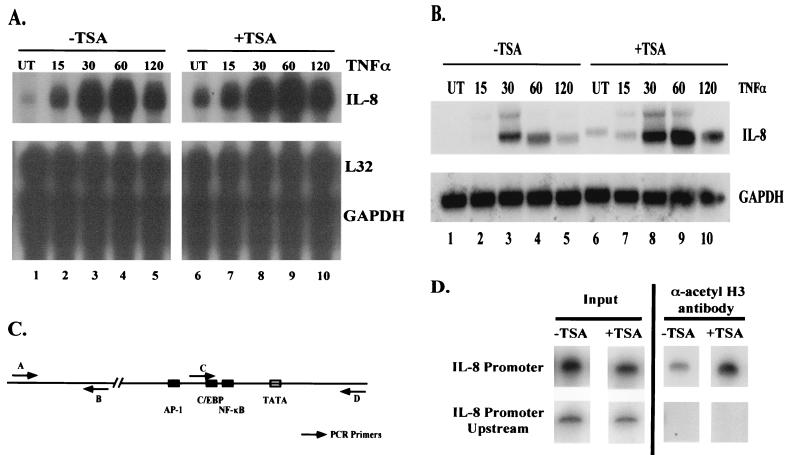
FIG. 8.
Inhibition of HDAC activity causes an increase in IL-8 expression. (A) Ribonuclease protection assay showing effect of TSA treatment on IL-8 expression. Total cellular RNA was harvested from HeLa cells after the indicated treatments and used in a ribonuclease protection assay. TNF-α was used at a final concentration of 10 ng/ml for the indicated times. TSA treatment was for 18 h at a final concentration of 100 nM. L32 and GAPDH are shown as loading controls. Other genes used in the assay are not shown. (B) Same as panel A, but RNA was used in Northern blot analysis to analyze the IL-8 expression pattern. (C) Diagram of IL-8 promoter and IL-8 upstream region. Arrows indicate primer pairs used in PCR for ChIP assays. (D) ChIP assay on IL-8 promoter and IL-8 upstream region. Cells were treated with either vehicle (dimethyl sulfoxide) or TSA for 18 h. DNA and protein were cross-linked with formaldehyde, and DNA was sheared and immunoprecipitated with anti-acetyl histone H3 antibody. After reversing cross-links, the DNA was amplified using end-labeled primers specific for the promoter region of the IL-8 gene or for a region upstream of the IL-8 promoter devoid of any known promoter elements. PCR products were analyzed by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and bands were visualized by autoradiography. Input, DNA prior to immunoprecipitation with the anti-acetyl histone H3 antibody. UT, untreated cells.