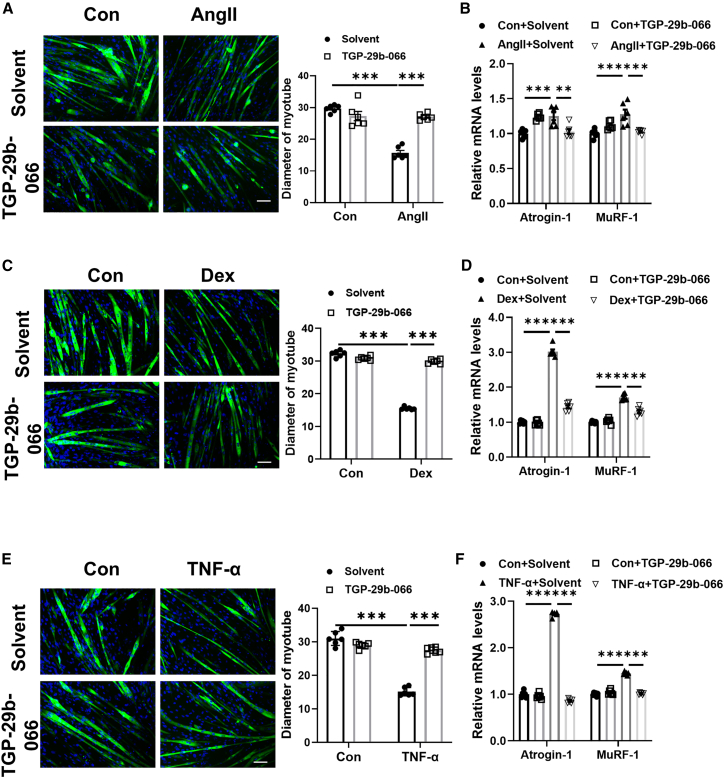
Figure 5.
TGP-29b-066 attenuates muscle atrophy in vitro
(A) Immunofluorescent staining and quantification of diameters of C2C12 myotubes treated with TGP-29b-066 in angiotensin II (Ang II)-induced muscle atrophy model (n = 6 per group; scale bar: 100 μm). (B) qRT-PCR analysis for the expression of Atrogin-1 and MuRF-1 in C2C12 myotubes treated with TGP-29b-066 in Ang II-induced muscle atrophy model (n = 6 per group). (C) Immunofluorescent staining and quantification of diameters of C2C12 myotubes treated with TGP-29b-066 in dexamethasone (Dex)-induced muscle atrophy model (n = 6 per group; scale bar: 100 μm). (D) qRT-PCR analysis for the expression of Atrogin-1 and MuRF-1 in C2C12 myotubes treated with TGP-29b-066 in Dex-induced muscle atrophy model (n = 6 per group). (E) Immunofluorescent staining and quantification of diameters of C2C12 myotubes treated with TGP-29b-066 in tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α)-induced muscle atrophy model (n = 6 per group; scale bar: 100 μm). (F) qRT-PCR analysis for the expression of Atrogin-1 and MuRF-1 in C2C12 myotubes treated with TGP-29b-066 in TNF-α-induced muscle atrophy model (n = 6 per group). Green: MF-20; blue: DAPI. Data are presented as mean ± SD. Statistical significance was determined by two-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey. ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001.