Fig. 1. Conventional σz-symmetric and twisted photonic crystal slab (PhCS) supporting BICs at the Γ point.
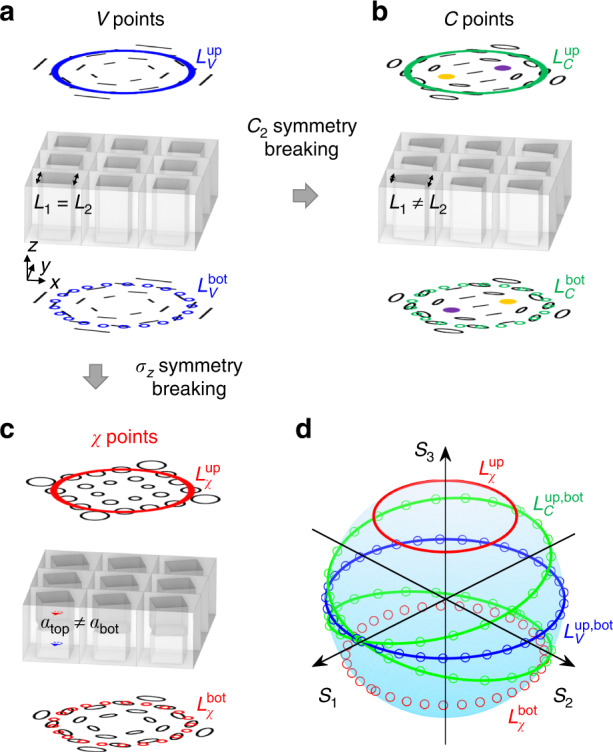
a Schematic of a conventional PhCS with etched square-hole standing in free space and its far-field polarization states distribution in momentum space near the V point at BIC. b Breaking in-plane inversion symmetry of the PhCS results in elimination of BIC and two C points spawning from the V point. The radiation in upward and downward remains the same. c The twisted PhCS by rotating the top hole with an angle of αtop. Breaking σz-symmetry results in asymmetric radiation of elliptical polarizations surrounding BIC upward and downward. The BIC is redefined as a χ point referring to arbitrary polarization states with the same ellipticity χ enclosing BIC. d Comparison of the polarization states on Poincaré sphere by enclosing the V point (blue line), C point (green line), and χ point (red line). The solid line and dash circles represent the encircling path in upward and downward direction, respectively
