Figure 2. Acidic bile salts inhibit activity of p53.
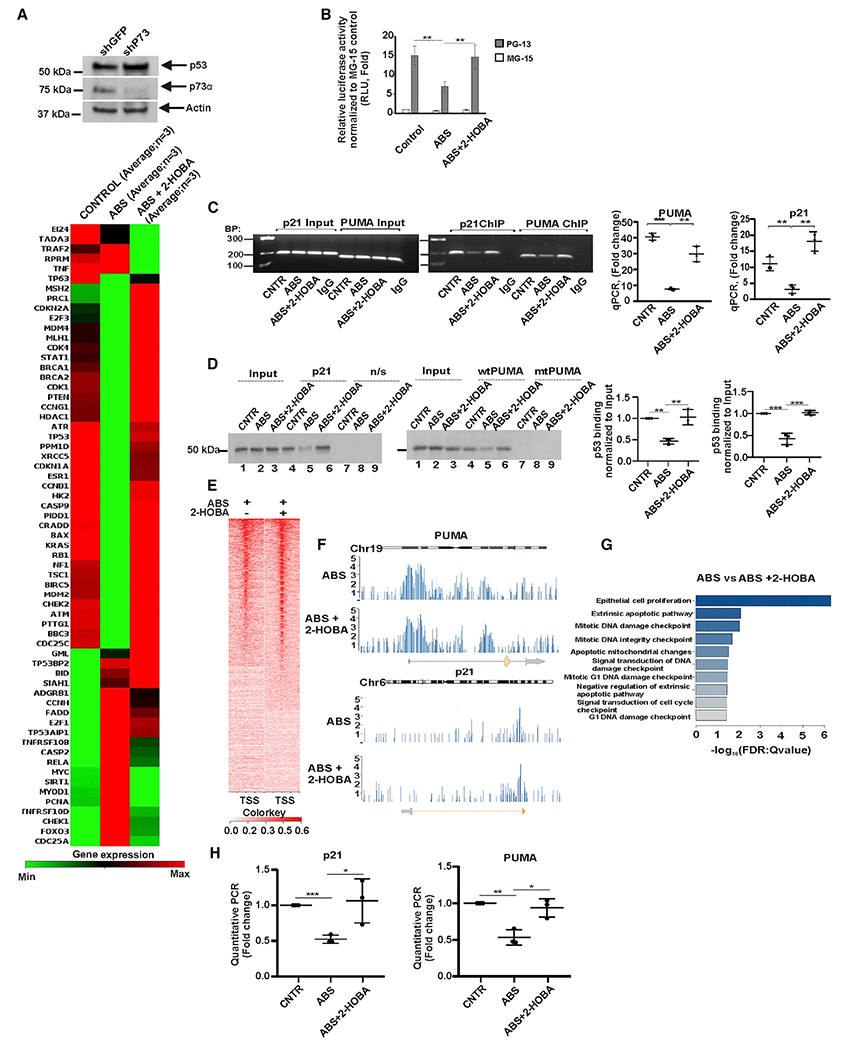
(A) Analysis of the p53 signaling pathway by PCR focus array in p73-deficient CP-A cells. The heatmap represents mRNA expression of 84 genes regulating the p53 signaling pathway (n = 3). Upper panel shows expression of p73 and p53 proteins.
(B) Analysis of p53 transcription activity in CP-A cells using the dual-luciferase reporter assay. PG13-Luc and control MG15-Luc p53 reporters were used. The endogenous p53 activity was significantly reduced by ABS treatment (control versus ABS, **p < 0.01) and 2-HOBA prevents effect of ABS (ABS versus 2-HOBA, **p < 0.01).
(C) ChIP analysis of p53 binding to the promoters of the CDKN1A(p21) (control versus ABS, **p < 0.01; ABS versus ABS+2-HOBA, **p < 0.01) and BBC3(PUMA) (control versus ABS, ***p < 0.001; ABS versus ABS+2-HOBA, **p < 0.01) genes in CP-A cells treated with ABS alone or in combination with 2-HOBA (n = 3; Student’s t test). The non-specific immunoglobulin (Ig)Gs were used as negative controls.
(D) DAI analyses of the p53 protein binding to the promoters of its target genes, CDKN1A(p21) (control versus ABS, **p < 0.01; ABS versus ABS+2-HOBA, **p < 0.01) and BBC3(PUMA) (control versus ABS, ***p < 0.001; ABS versus ABS+2-HOBA, ***p < 0.001; n = 3; Tukey’s multiple comparison; n/s, non-specific DNA probe). Binding of p53 protein in control cells was arbitrarily set at 1.
(E) Next generation sequencing (NGS) plot shows ChIP-seq binding profile in ABS and ABS+2-HOBA treated CP-A cells. TSS, transcription start site.
(F) ChIP-seq binding peaks in ABS- and ABS+2-HOBA-treated CP-A cells.
(G) The gene ontology analysis of biological processes using the aforementioned ChIP-seq data.
(H) Real-time qPCR analysis of p21 and PUMA mRNA expression in p73-deficient CP-A cells treated with ABS. Levels of p21 and PUMA mRNAs were decreased after ABS treatment, p21 mRNA (control versus ABS, ***p < 0.001) and PUMA mRNA (control versus ABS, **p < 0.01), whereas 2-HOBA prevented the effect of ABS treatment (n = 3; Student’s t test). Expression of p53 mRNA in untreated cells was arbitrarily set at 1. All results are expressed as mean ± SD. See also Figure S2A.
