Figure 3. Acidic bile salts increase the formation of isoLG-p53 adducts.
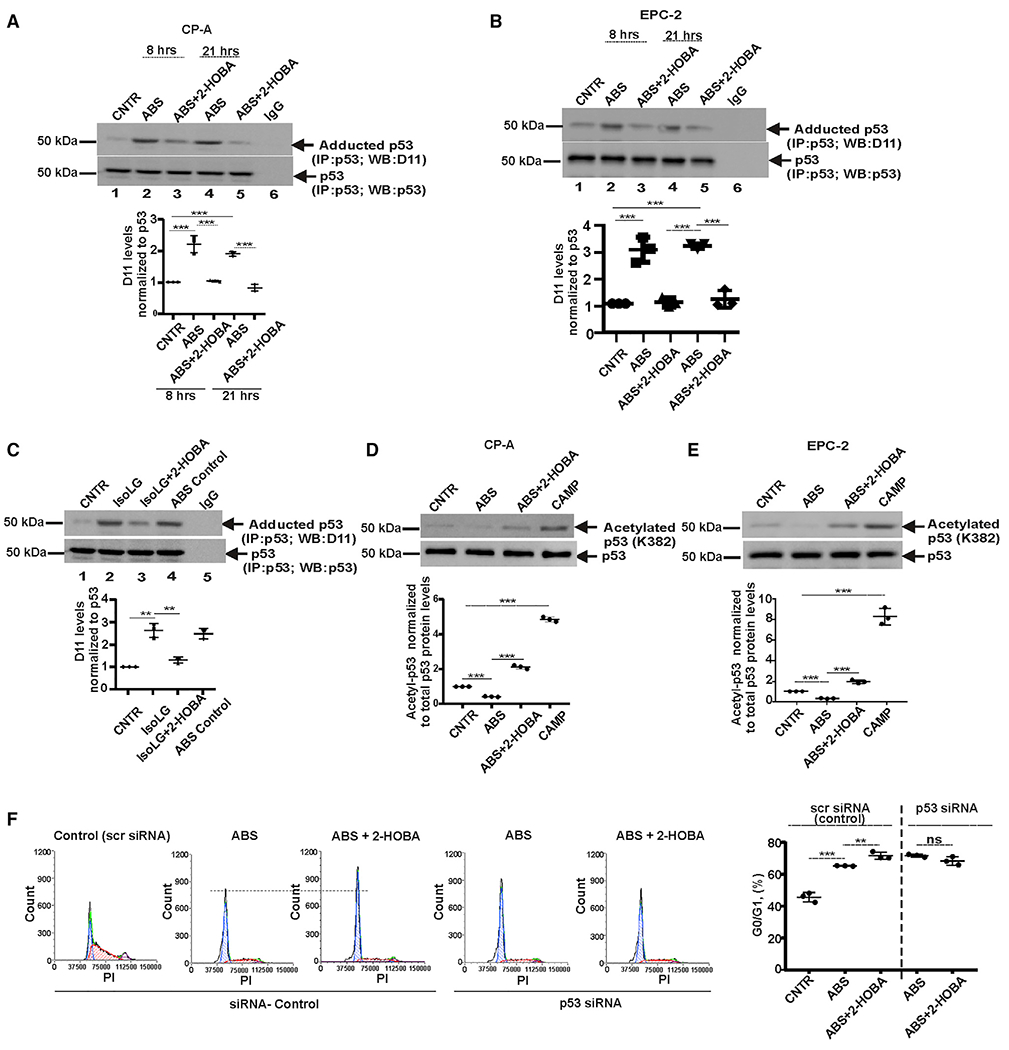
(A) p53 protein was immunoprecipitated from CP-A cells and analyzed for adduction of p53 protein with D11 scFv antibody by western blotting. ABS treatment increases levels of isoLG-p53 protein adducts, while 2-HOBA counteracts this effect by preventing the isoLG adduction of p53 protein (n = 3; Tukey’s multiple comparison) at 8 h (control versus ABS, ***p < 0.001; ABS versus ABS+2-HOBA, ***p < 0.001) and 21 h (control versus ABS, ***p < 0.001; ABS versus ABS+2-HOBA, ***p < 0.001). Levels of isoLG: p53 adducts was normalized to total levels of p53 protein, which were analyzed with p53(D01) antibody. Levels of p53 protein adduction in control cells was arbitrarily set at 1.
(B) The same as (A) but the p53 protein adduction was analyzed in EPC-2 cells at 8 h (control versus ABS, ***p < 0.001; ABS versus ABS+2-HOBA, ***p < 0.001) and 21 h time points (control versus ABS, ***p < 0.001; ABS versus ABS+2-HOBA, ***p < 0.001) after treatment.
(C) CP-A cells were treated with 0.5 μM synthetic isoLGs and analyzed for the adduction of p53 protein (control versus isoLG, **p < 0.01; isoLG versus isoLG+2-HOBA, **p < 0.01; n = 3; Tukey’s multiple comparison).
(D) Analyses of p53 protein acetylation in CP-A cells by western blotting with antibody recognizing acetylated p53 at Lys382 (control versus ABS, ***p < 0.001; ABS versus ABS+2-HOBA, ***p < 0.001; n = 3; Tukey’s multiple comparison).
(E) The same as (D) but acetylation of p53 protein was analyzed in EPC-2 cells (control versus ABS, ***p < 0.001; ABS versus ABS+2-HOBA, ***p < 0.001; n = 3; Tukey’s multiple comparison).
(F) Cell-cycle analysis in CP-A cells transfected with either p53 siRNA or scrambled siRNA and treated with ABS alone or in combination with 2-HOBA. Cell cycle was analyzed by flow cytometry and compared between groups (scr siRNA: ABS versus ABS+2-HOBA, **p < 0.01; p53 siRNA: ABS versus ABS+2-HOBA; NS, not significant; n = 3; Tukey’s multiple comparison). All results are expressed as mean ± SD.
