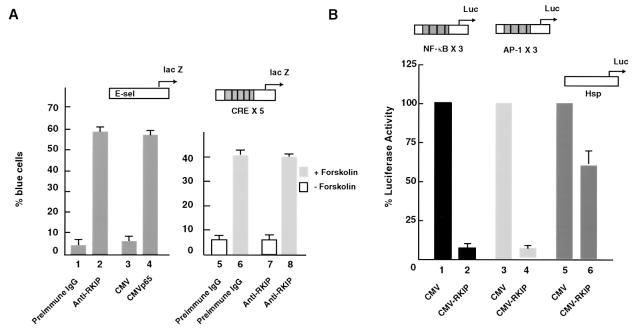
FIG. 1.
Ablation of RKIP activates and overexpression of RKIP represses basal NF-κB activity. (A) Ablation of RKIP activity by antibody injection activates an NF-κB-dependent reporter (E-sel) but not a cyclic AMP-stimulated reporter (CRE × 5). E-sel is an E-selectin promoter DNA fragment containing one copy of the consensus NF-κB binding site (71). Quiescent Rat1 cells were microinjected with the indicated reporter plasmids and antibodies and either left unstimulated or treated with 20 μg of forskolin per ml, an activator of adenyl cyclase. (B) Overexpression of RKIP represses NF-κB- and AP-1-dependent reporters. RKIP was placed under the control of the cytomegalovirus (CMV) promoter (CMV-RKIP). RKIP or an empty vector control (CMV) was cotransfected with the indicated reporter plasmids into exponentially growing NIH 3T3 cells, and 48 h later extracts were assayed for luciferase activity. The activities of reporters in combination with the empty CMV vector were set to 100%. In all panels the means and standard deviations of at least two independent experiments are shown.