Fig. 5.
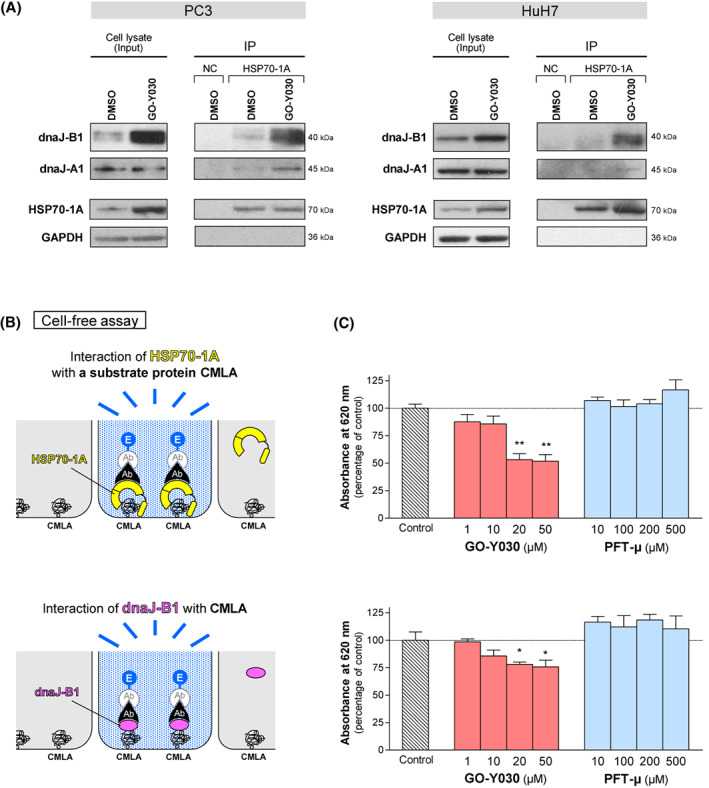
Inhibitory effect of GO‐Y030 on the substrate‐recognition and ‐binding activity of both HSP70‐1A and dnaJ‐B1. (A) Co‐immunoprecipitation (Co‐IP) of HSP70‐1A in PC3 (left) and HuH7 (right) cell lysates. Whole cell lysates were prepared from the cell lines that had been treated with GO‐Y030 (2 μm) or dimethylsulfoxide for 24 h. Immunoprecipitation and western blot analysis using the indicated antibodies revealed that HSP70‐1A interacted with HSP40 family proteins such as dnaJ‐A1 and dnaJ‐B1 even after treatment with GO‐Y030. These data suggest that GO‐Y030 should not affect the association between HSP70‐1A and HSP40s. Input was 3% of total protein extract used in the assay. Negative controls (NC) were performed by using an isotype and concentration matched non‐specific control antibody. (B) Schematic diagram for the substrate‐binding activity assay. Interaction of HSP70‐1A (upper) or dnaJ‐B1 (lower) with the substrate protein carboxymethylated α‐lactalbumin (CMLA), which is permanently unfolded, was measured using a modified enzyme‐linked immunosorbent assay. The substrate‐binding activity was determined as the enzymatic activity of alkaline phosphatase. (C) Although GO‐Y030 reduced the binding of not only HSP70‐1A (upper) but dnaJ‐B1 (lower) to CMLA in a dose‐dependent manner, treatment with PFT‐μ did not show any significant differences. The data are acquired as percentage of absorbance of control group treated with dimethylsulfoxide alone. Statistical significance was calculated using Student's t‐test. Data represent the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 compared to the control group (dimethylsulfoxide alone). Ab, antibody; E, enzyme.
