Figure 1. Human monoclonal antibodies isolated from two clinical studies on Pfs230D1-EPA vaccines possess diverse variable gene usage, functional activity and epitope bins.
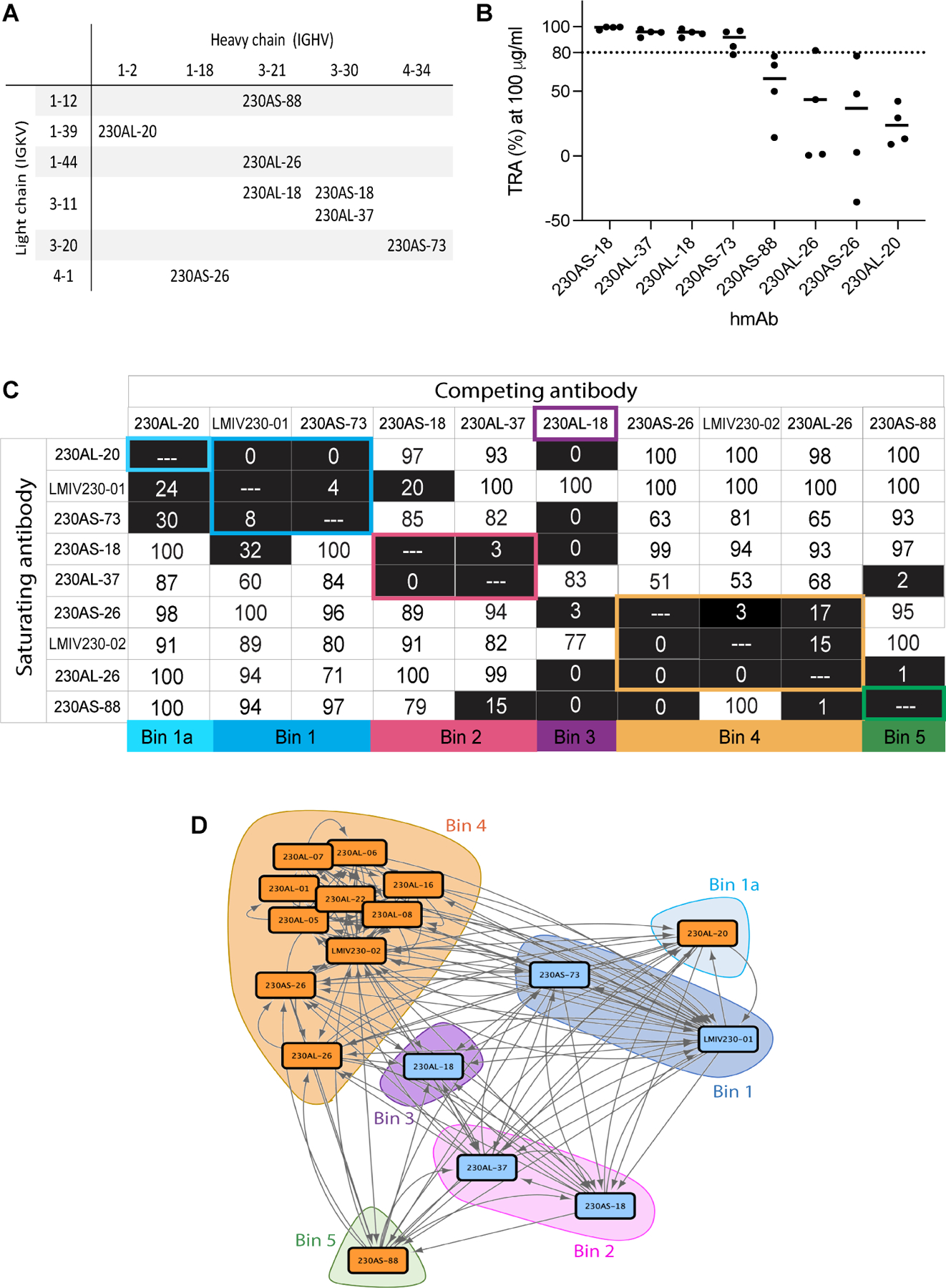
A) Variable gene usage of 8 hmAbs isolated in the present study. B) Transmission-reducing activities (TRA) of individual hmAb. Data are the results of four separate feeds in the presence of human complement. The best estimated percentage TRA for each hmAb is depicted in bars. C) Epitope binning of human anti-Pfs230D1 scFvs. Biotinylated Pfs230D1 was immobilized on biosensors. Saturating scFvs are listed on the left and the competing scFvs are listed on the top. Reported scores are a percentage of total binding response of that scFv in the absence of competitor scFv. Values <50% are shaded in black. Any experiments with >100% and <0% were given a score of 100 and 0, respectively. Potential epitope bins are grouped and highlighted. D) Network analysis of epitope binning for seventeen hmAbs isolated from two immunization schemes of Pfs230D1-EPA. Data for eight hmAbs are reported in the current study and data for an additional nine reported previously 26. The blue and orange nodes represent potent and non-potent transmission-reducing hmAbs, respectively, and arrows depict epitope binning orientation with the length of the connection weighted by percent binding.
