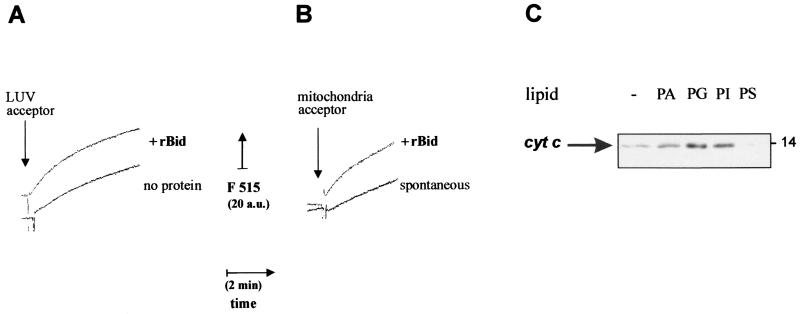
FIG. 3.
Correlation between lipid transfer and release of cytochrome c by recombinant Bid. (A) Lipid transfer was measured as time courses with sonicated donor liposomes prepared with a 1:3 (wt/wt) mixture of BODIPY FL C5-HPA with phospholipids (50% PC, 25% PI, and 25% PS) and acceptor liposomes consisting of LUV. These LUV were prepared by filter extrusion (38) with a phospholipid mixture closely resembling that of the OM (8, 25), namely, 50% PC, 30% PE, 12.5% PI, 5% PG, and 2.5% CL. Before the assay, both donor and LUV liposomes were purified by gel filtration with a Sigma PD10 column. Donor liposomes were equilibrated in assay buffer at a final concentration of 30 nM, and then 2 μg of LUV acceptors per ml were added in either the absence (bottom trace) or the presence (top, trace) of 250 ng of recombinant mouse Bid (rBid) per ml (i.e., 10 nM). Fluorescence emission at 515 nm was continuously monitored with excitation at 490 nm. (B) Lipid transfer from sonicated donor liposomes was measured as shown in panel A using 2.5 μg of mouse liver mitochondria per ml as acceptor membranes. The spontaneous rate of transfer (bottom trace) was accelerated when 30 nM recombinant mouse Bid (rBid) was coincubated with donor liposomes prior to the addition of mitochondria (top trace) (C) Mouse liver mitochondria were incubated for 15 min with 10 nM recombinant Bid in assay buffer. Except for the control sample (−), mitochondria were also incubated with 0.1 mg/ml liposomes formed by different negatively charged phospholipids and then separated by centrifugation as in the experiment shown in Fig. 1C. Equal volumes of the supernatants were immunoblotted for cytochrome c as in routine cell-free assays (22).