Fig. 5. EJCs and RNPS1 protect proximal RNA regions from aberrant mRNA processing.
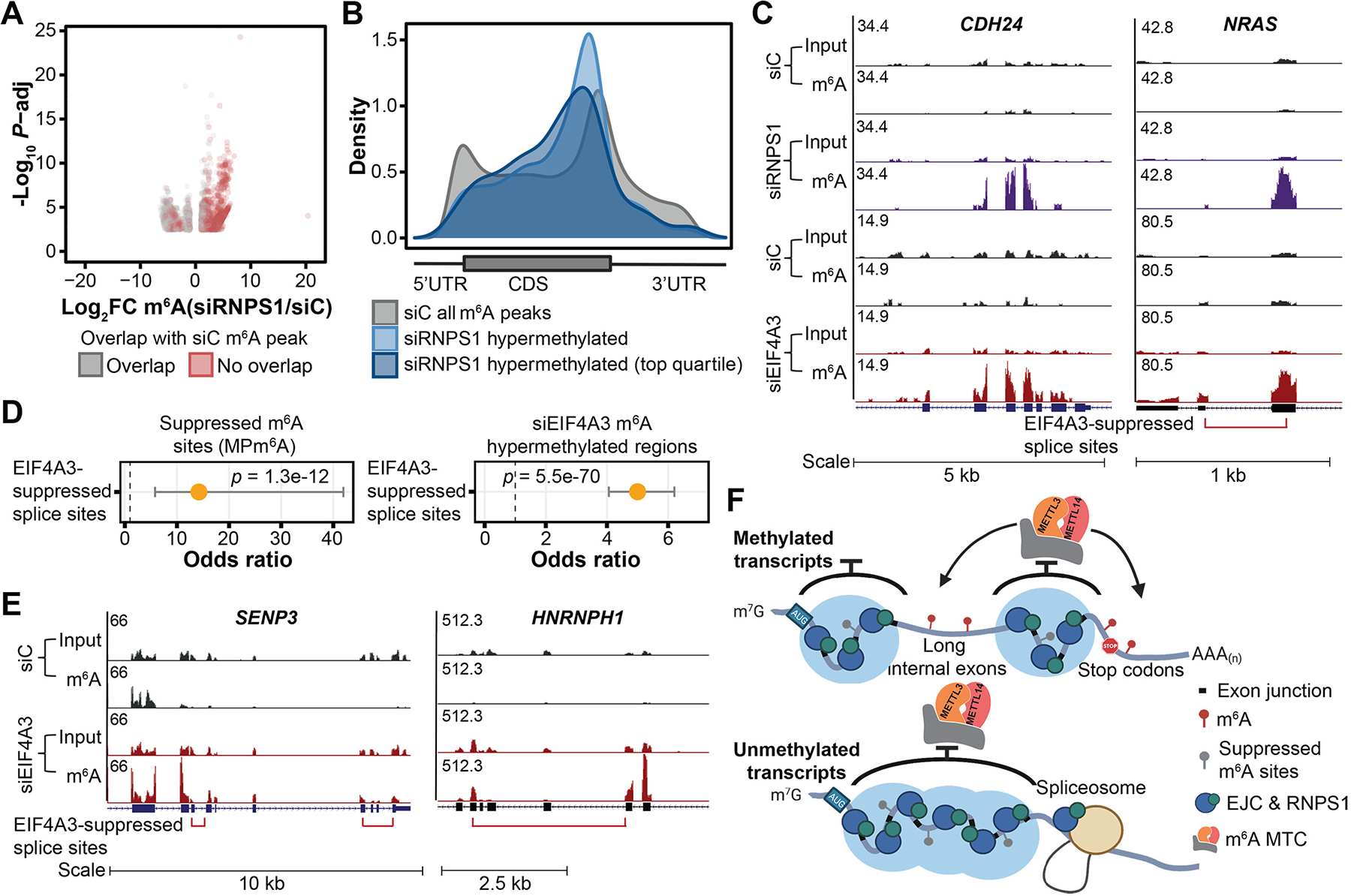
(A) Differentially methylated regions upon RNPS1 KD in HeLa cells (FDR < 0.1, |log2FC| > 1), three biological replicates. Gray and red dots indicate differentially methylated regions that overlap and do not overlap with m6A peaks in the control KD cells, respectively. (B) Metagenes of significantly m6A hypermethylated regions (and top quartile) upon RNPS1 KD in HeLa cells in comparison with that of all m6A peaks in control cells. (C) Input and m6A-IP read coverage at CDH24 and NRAS upon RNPS1 KD and EIF4A3 KD, respectively, as well as corresponding controls in HeLa cells. (D) Enrichment of suppressed m6A sites (identified from MPm6A) at EIF4A3-suppressed splice sites (left) and enrichment of EIF4A3 KD hypermethylated regions at EIF4A3-suppressed splice sites (right). Fisher’s exact test, dot and bar represent odds ratio and 95% confidence interval. (E) Input and m6A-IP read coverage at SENP3 and HNRNPH1 in EIF4A3 KD and control HeLa cells. (F) Schematic model depicting that EJCs and RNPS1 (and potentially other EJC-associated proteins) protect exon junction-proximal RNA from m6A deposition through local mRNA packaging. For (C) and (E), red bracket indicates EIF4A3-suppressed splice variant, with ends of bracket indicating the suppressed splice junctions.
