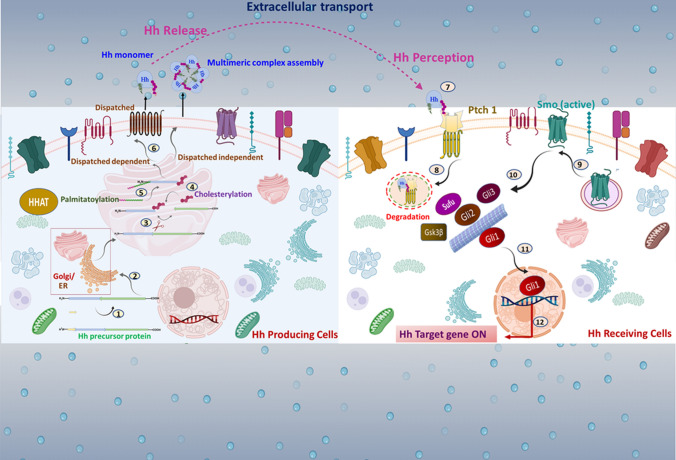
Fig. 1.
Insight on molecular events involved in Hh signal transmission: in Hh-producing cells, the Hh transcript is translated as a ~ 45 kDa pro-protein consisting of a signal sequence at the N-terminal domain followed by the C-terminal domain. Multiple steps are implicated in Hh signal transmission: 1. The signal sequence is removed. 2. Hh polypeptides are moved into the ER and the Golgi apparatus (A rectangular magnified box represents it). 3. Hh pro-protein undergoes autocatalytic processing 4. The N-terminal half of Hh is covalently anchored with cholesterol via cholesterylation. 5. A palmitoyl group is transferred to Hh’s extreme N-terminus cysteine using HHAT. 6. In the extracellular space, the mature Hh is secreted distinctly as a Disp-dependent monomer or a Disp-independent multimer. 7. Hh reaches the surface of target cells. 8. In Hh receiving cells, Hh complexes with Ptch1, leading to internalization. 9. Smo is released from Ptch1-mediated suppression, and free Smo translocates into the membrane 10. Activation of Smo regulates Gli family proteins, such as Gli1, Gli2, and Gli3, with the help of multiple protein kinases. 11. An active form of Gli, such as Gli1, trans-locates into the nucleus. 12. Gli triggers activation of downstream targets