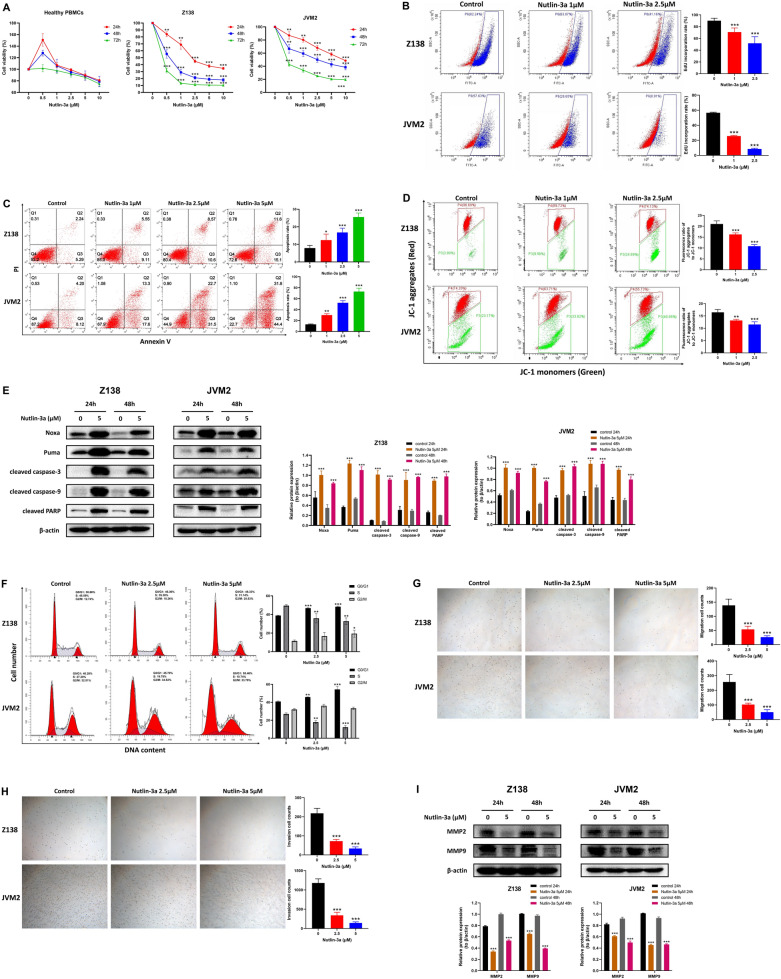
Fig. 5.
Nutlin-3a treatment led to attenuated cell proliferation, migration and invasion as well as enhanced apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in Z138 and JVM2 cells. A After healthy PBMCs, Z138 and JVM2 cells exposed to 0.5 μM, 1 μM, 2.5 μM, 5 μM and 10 μM nutlin-3a for 24 h, 48 h and 72 h, cell viability was assessed by CCK-8 assay. B After Z138 and JVM2 cells treated with 1 μM and 2.5 μM nutlin-3a for 48 h, EdU incorporation rate was detected by flow cytometry to determine the cell proliferation condition. C After Z138 and JVM2 cells treated with 1 μM, 2.5 μM and 5 μM nutlin-3a for 48 h, the apoptosis rate was quantified by flow cytometry based on Annexin V-FITC/PI staining. D The changes of MMP in Z138 and JVM2 cells was examined by flow cytometry based on JC-1 fluorescent probe after exposed to 1 μM and 2.5 μM nutlin-3a for 48 h. E Targeted protein expression by WB analysis after 24 h and 48 h 5 μM nutlin-3a treatment in Z138 and JVM2 cells. F The proportion of G0/G1, S and G2/M phases in the cell cycle was analyzed by PI flow cytometry after Z138 and JVM2 cells treated with 2.5 μM and 5 μM nutlin-3a for 48 h (Z138) or 72 h (JVM2). G, H After treatment with 2.5 μM and 5 μM nutlin-3a for 48 h in Z138 and JVM2 cells, the effect of nutlin-3a on cell migration (G) and invasion (H) was confirmed by Transwell assays. Images were captured by an inverted microscope (× 10 magnification). I Migration and invasion-related proteins were analyzed by WB after 24 h and 48 h nutlin-3a treatment in Z138 and JVM2 cells. The above data were obtained from at least three independent experiments and presented as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 compared with the control group