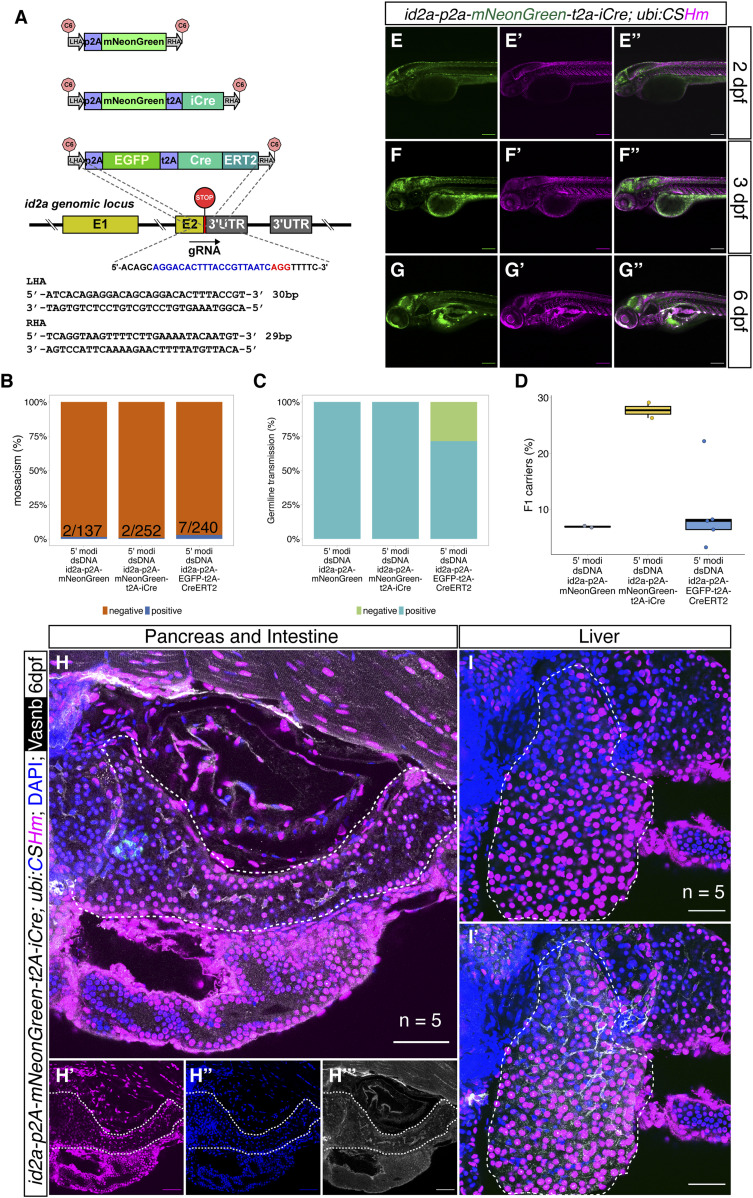
Figure 5. The design and characterization of knock-in lines at the id2a locus.
(A) The design of the donor dsDNA template and gRNA sequence for the construction of knock-in lines at the 3′ end of the id2a locus. The nucleotide sequence in blue indicates gRNA, whereas the nucleotide sequence in red indicates the PAM sequence. The bottom panel shows the sequences of LHA and RHA. (B, C, D) Summary statistics of id2a knock-in efficiency, including the percentage of injected F0 with observable fluorescence labelling in the hindbrain, spinal cord, and olfactory organs (B), the percentage of adult F0 giving rise to germline transmission (C), and the percentage of F1 siblings carrying the knock-in cassettes (D). (E, F, G) Representative confocal images of TgKI(id2a-p2A-mNeonGreen-t2A-iCre); Tg(ubi:CSHm) at 2 dpf (E, E’, E’’), 3 dpf (F, F’, F’’), and 6 dpf (G, G’, G’’). Cells that are mNeonGreen positive indicate id2a-expressing cells, whereas the progenies of the id2a lineage were mCherry labelled. (H, I) Representative confocal images of lineage-tracing experiments in the zebrafish larval pancreata (H, H’, H’’, H’’’), intestine (H, H’, H’’, H’’’), and liver (I, I’) in the TgKI(id2a-p2A-mNeonGreen-t2A-iCre);Tg(ubi:CSHm) line. We scanned five pancreata and livers, with 26–34 single planes imaged. Cells in cyan are α-cells based on anti-Glucagon antibody staining. (E, F, G, H, I) Scale bars = 200 μm (E, F, G) or 80 μm (H, I).