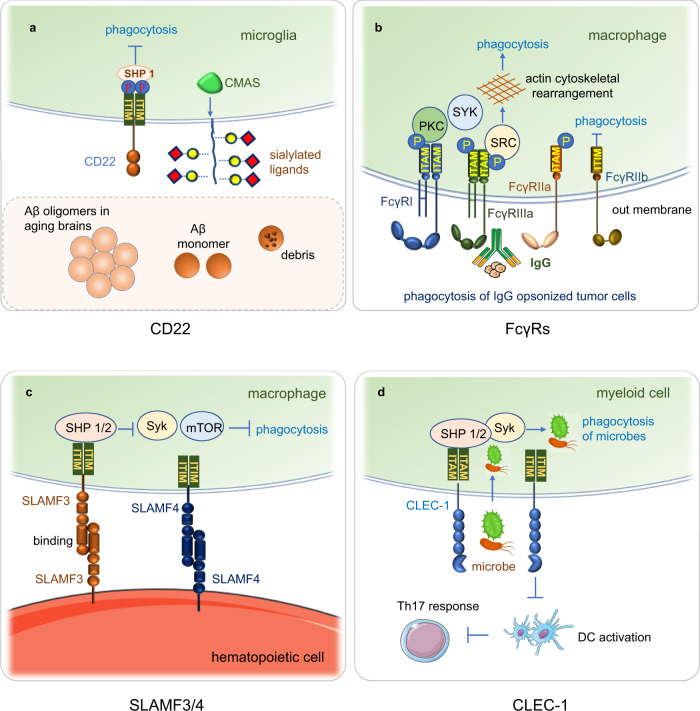
Fig. 3.
The phagocytosis receptors CD22, Fc receptors, SLAMF3/4 and CLEC1. a CD22 binds α2,6-linked sialic acid and recruits tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1 to inhibit the phagocytic capacity of microglia. The anti-CD22 treatment enhanced clearance of injected oligomeric amyloid-β (Aβ), myelin debris and α-synuclein fibrils in aging brains. CMAS is a key synthase functioning in sialic acid synthesis, related to CD22 function. b FcγRIIb, FcγRI, FcγRIIIa, and FcγRIIa are expressed on macrophages. FcγRs crosslink IgG immune complex triggers phosphorylation of their ITAMs and activates kinases of SYK, SRC and PKC pathway, kinase activation leads to actin remodeling, which is crucial for phagocytosis of the IgG immune complex. FcγRIIB is the only phagocytosis-inhibitory receptor, and the other family members are phagocytosis-activating receptors within the human FcγR family. FcγRIIB contains an ITIM in its cytoplasmic region, and the phosphorylation and activation of the ITIM recruit the phosphatases SHP1 and SHP2 and inhibit downstream phagocytosis. c SLFRs are ubiquitously expressed in hematopoietic cells. SLAMF3 and SLAMF4 were identified as “don’t eat me” receptors on macrophages. They inhibit “eat me” signals, such as lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 (LRP1) -mediated activation of mTOR and Syk to macrophages through SH2 domain-containing phosphatases and hematopoietic cells without SFRs are easily phagocyted by macrophages. d CLEC-1 is expressed primarily by myeloid cells, CLEC-1 on human DC dampens DC activation and restrains downstream Th17 responses, CLEC-1 is a novel myeloid immune checkpoint limiting tumor cells’ phagocytosis and tumor antigen presentation. CLRs binding to microbial surfaces influence phagocytosis by promoting inflammatory signals and triggering intracellular signaling to induce phagocytosis of microbes