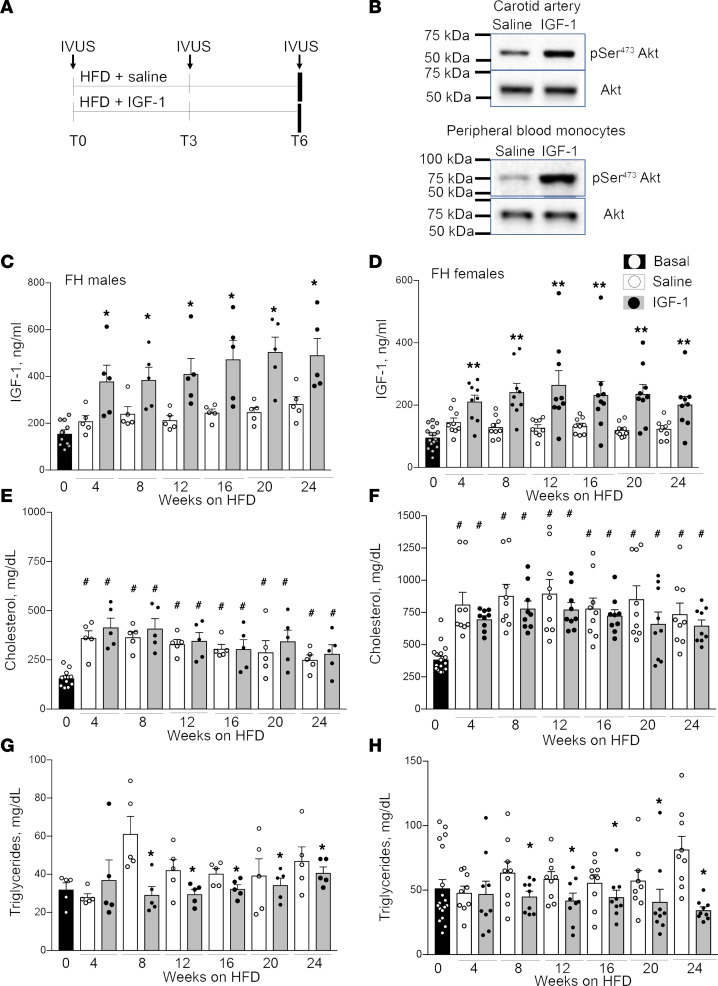
Figure 1. Phenotype of FH pigs.
(A) Experimental design. FH pigs were injected daily with 50 μg/kg human recombinant IGF-1 or saline (control) (males, n = 5/group; females, n = 9/group) and fed with high-fat diet (HFD) for 6 months. Coronary atherosclerosis was quantified by intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) before injections (T0), after 3 months (T3), and after 6 months (T6, at sacrificing). (B) IGF-1 stimulated specific downstream signaling in porcine carotid artery and in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC). IGF-1 (or saline) was injected into pig, carotids and blood were collected 4 hours following injections, and Akt phosphorylation was quantified by immunoblotting. (C–H) Blood was collected at basal level (T0) and each month during injections (total 7 time points). Total plasma IGF-1 level was quantified by ELISA in FH males (C) and females (D). Cholesterol (E and F) and triglyceride (G and H) levels in IGF-1– and saline-injected male (left) and female (right) FH pigs. Males: n = 10 for basal, and n = 5/group for each time point. Females: n = 18 for basal, and n = 9/group for each time point. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, vs. saline based on t test, #P < 0.05 vs. basal level based on 3-way ANOVA.