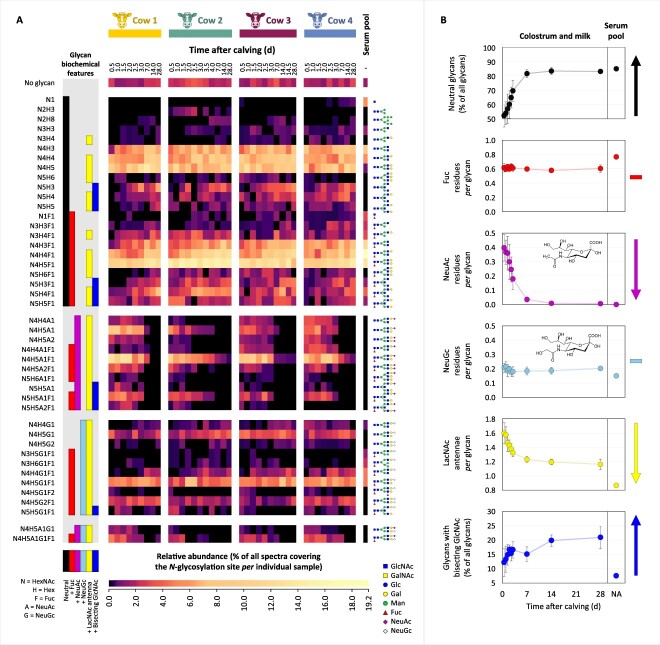
Fig. 4.
Changes in the N-glycosylation profiles of bovine IgG in the interval 0.5–28 d after calving in the bovine milk of the four cows, i.e. cow 1, cow 2, cow 3 and cow 4. Additionally, in the last column, for comparison, the N-glycosylation profile of bovine serum IgG is depicted (pooled sample). (A) Heatmap depicting the macro- and microheterogeneity of the IgG CH2 domain N-glycosylation determined based on spectral counts. Normalization was performed relative to all spectra covering the glycosylation site, whereby the sum of all glycoforms and the non-glycosylated site amounts to 100 percent, and the relative quantitation of the non-glycosylated site indirectly indicates site occupancy. Clustering was performed based on the biochemical features of the N-glycans: neutral (black), fucosylated (red), sialylated with NeuAc (magenta), sialylated with NeuGc (light blue), containing LacNAc antennae (yellow) or bisecting GlcNAc (blue), respectively. The glycan composition is indicated to the left of the heatmap. To the right of the heatmap are proposed glycan structures corresponding to each glycan composition. (B) Illustrative lactation dynamics of the N-glycan biochemical features averaged across the four cows and compared to their corresponding level in the bovine serum IgG, with the panels from top to bottom describing the changes in neutral glycans, fucosylation, sialylation with NeuAc or NeuGc, containing LacNAc antennae or bisecting GlcNAc, respectively. The error bars represent the standard deviation of values from the four cows. The colour codes of the biochemical features are consistent between panels (A) and (B). Abbreviations: Gal = galactose; Glc = glucose; man = mannose; hex = hexose; GalNAc = N-acetylgalactosamine; GlcNAc = N-acetylglucosamine; HexNAc = N-acetylhexosamine; Fuc = fucose; NeuAc = N-acetylneuraminic acid; NeuGc = N-glycolylneuraminic acid.