Figure 4. Rescue of hypomorphic malonyl-CoA-acyl carrier protein transacylase (MCAT) mutant C2C12 with wild-type (WT) and p.T271I mutant MCAT constructs.
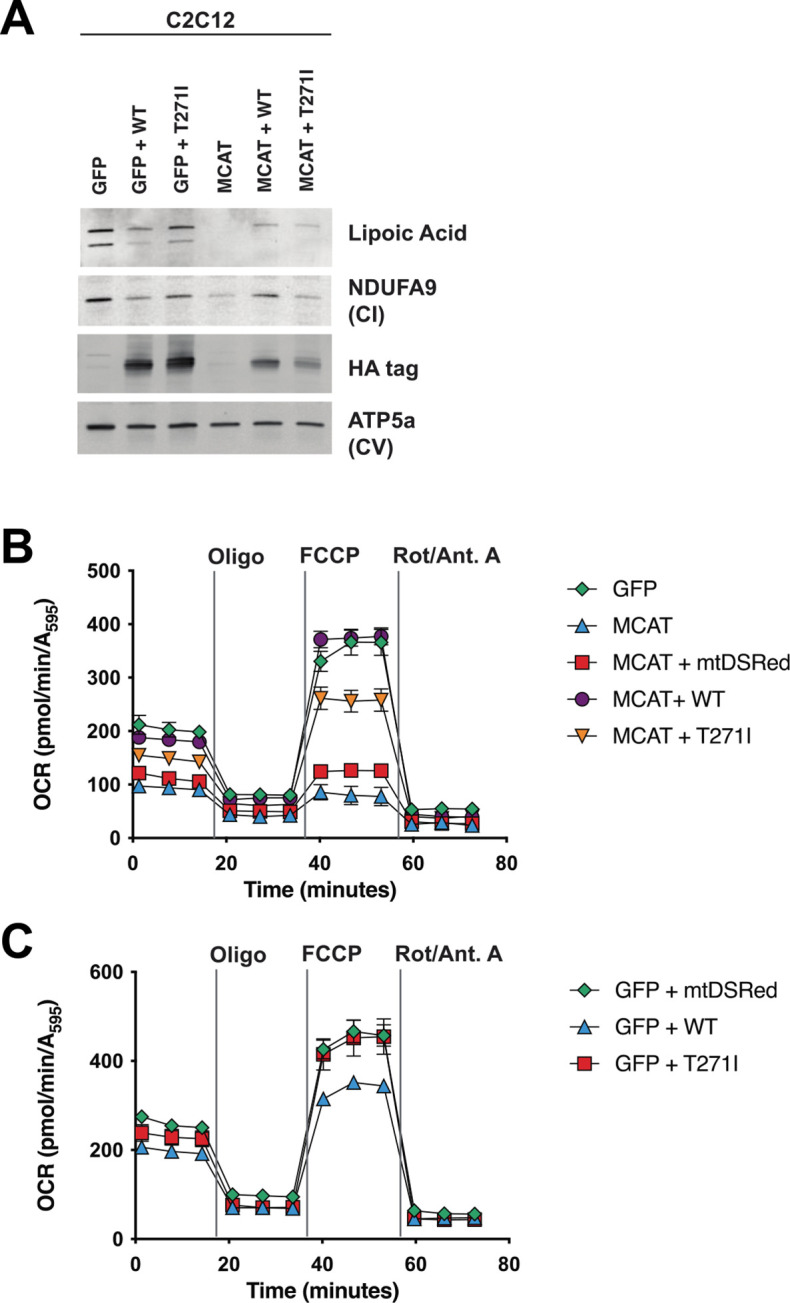
(A) Mitochondrial lysates generated from MCAT hypomorphic CRISPR mutant C2C12 mouse skeletal myoblasts (MCAT) and isogenic controls (GFP), stably infected with either WT human MCAT or p.T271I mutant human MCAT (T271I) transgenes. Lysates were separated by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. Protein lipoylation (lipoic acid) is undetectable in MCAT mutant C2C12 and rescued by both WT and p.T271I mutant MCAT, while complex I (NDUFA9, CI) is only rescued by expression of WT human MCAT. For each immunoblot, at least two technical replicates were completed and one representative blot is shown. (B–C) Cells from each of the indicated genotypes were seeded in eight wells of a 96-well seahorse plate and allowed to adhere overnight, then equilibrated and treated with the indicated drugs following standard mitochondrial stress test protocols from the manufacturer to determine oxygen consumption rate (OCR). Error bars are SEM. Oxygen consumption is fully rescued by WT human MCAT but only partially rescued by expression of the p.T271I patient mutation.
