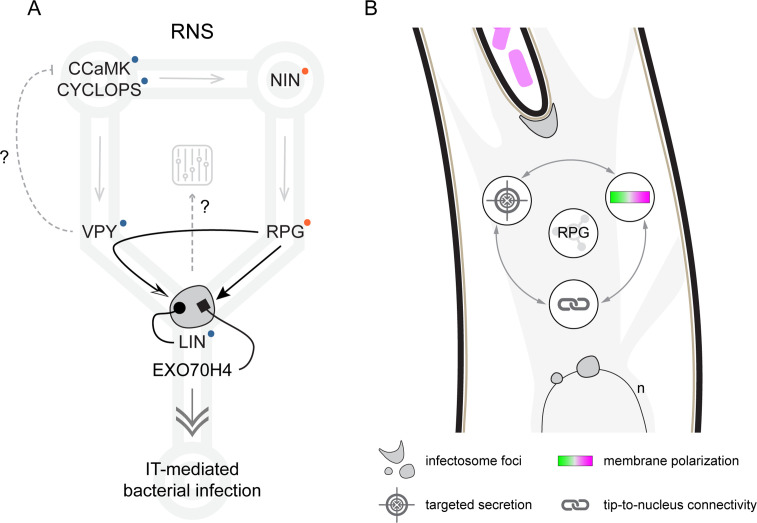
Figure 7. Proposed model for Rhizobium-directed polar growth (RPG) role during intracellular rhizobial infection.
(A) During Root Nodule Symbiosis (RNS), NIN-dependent transcription of RPG (gray arrow, Liu et al., 2019a; Soyano and Hayashi, 2014) leads to accumulation of the encoded protein (black arrow) within infectosome foci hosting VAPYRIN (VPY), LUMPY INFECTION (LIN), and EXO70H4 (gray irregular round shape, this study, Liu et al., 2019a). The coalescence of VPY into cytoplasmic foci is fully dependent on RPG (curved arrow, this study), while LIN is required to stabilize VPY (dotted arrow, Liu et al., 2019a, Liu et al., 2021). Since VPY and LIN belong to a conserved endosymbiotic signaling pathway including the core components CCaMK and CYCLOPS (Radhakrishnan et al., 2020, blue dots), we propose that RPG serves as a specificity determinant for infectosome-related endo- and exocytotic events (double arrow) enabling IT-mediated rhizobial infection. This is further supported by the capacity of RPG to interact with the exocyst subunit EXO70H4 (rectangular arrow). RPG-dependent segregation of VPY in infectosome foci might additionally allow to modulate the symbiotic signaling circuit (gray dashed arrow), if the putative negative regulation exerted by VPY on CCaMK (dashed gray flat arrow) during AM (Lindsay et al., 2022) would be conserved during RNS. Gray arrows indicate transcriptional activation/dependency (according to Murray et al., 2011; Singh et al., 2014; Liu et al., 2019a; Li et al., 2023). Orange dots indicate loss of the corresponding gene in non-nodulating species of the FaFaCuRo clade. (B) RPG represents a protein hub for infectosome assembly and its function is required to maintain a functional interplay between membrane polarization, tip-to-nucleus connectivity, and targeted secretion enabling infection thread (IT) polar progression.