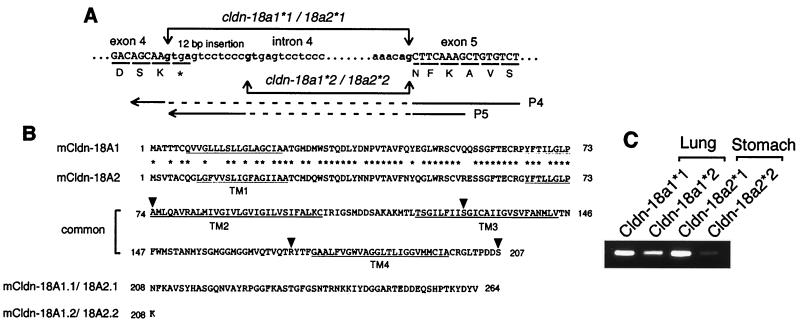
FIG. 2.
(A) Alternative splicing of the mouse claudin-18 gene between exons 4 and 5. The intron 4,5′-splice donor gt, and 3′-splice acceptor ag are in boldface. Amino acid residues are shown below each underlined codon, and the termination codon is marked with an asterisk. The claudin (cldn)-18a1∗1/18a2∗1 gene encodes the amino acid sequence DSNFK at the exon-intron junction, whereas the claudin-18a1∗2/18a2∗2 gene encodes the amino acid sequence DSK. The P4 primer has a continuous sequence of exons 4 and 5 without alternative insertion, and P5 is an alternative insertion-specific primer. The primer sequences are indicated by solid lines. Primer pairs P3-P4 and P3-P5 (Fig. 1) produce fragments specific to claudin-18a1∗1/2∗1 and claudin-18a1∗2/2∗2, respectively. (B) Deduced amino acid sequences of four types of claudin-18 polypeptides. The locations of the putative transmembrane domains are underlined and indicated as TM1 to TM4. Amino acids that are identical in claudin-18A1 and -18A2 are indicated by asterisks. The exon-intron junctions are indicated by arrowheads. (C) RT-PCR confirmation of expression of the four types of transcripts. Products obtained with primer pairs P3-P4 and P3-P5 using mouse adult lung and stomach mRNAs are shown.