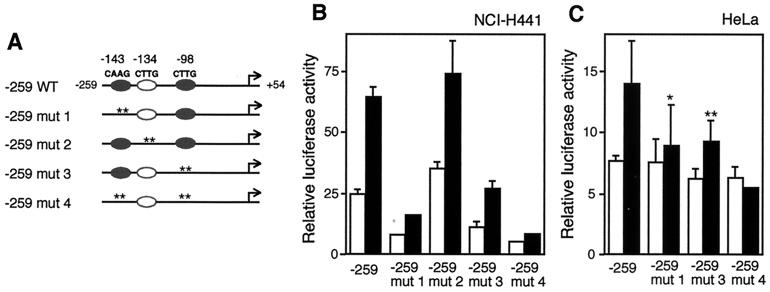
FIG. 6.
Mutation of T/EBP/NKX2.1 binding sites reduces trans activation by T/EBP/NKX2.1. (A) Schematic representation of wild-type (−259 WT) and mutant (−259 mut 1 to 4) constructs. Closed ovals represent potential T/EBP/NKX2.1 binding sites. Open ovals depict functionless T/EBP/NKX2.1 binding consensus sites. Site-specific mutations are indicated by asterisks (each asterisk corresponds to a nucleotide). The mutated sequences are shown in Fig. 7A. (B and C) The deletion −259 construct with or without various site-specific mutations was transiently transfected into NCI-H441 cells (B) or HeLa cells (C) in the presence of coexpressed pCMV4-T/EBP/NKX2.1 (black bars) or pCMV4 (white bars). Values represent the means ± SD from three separate experiments. ∗, significantly different from construct −259 with the expression vector at a P value of <0.01; ∗∗, significantly different from construct −259 with the expression vector at a P value of <0.05.