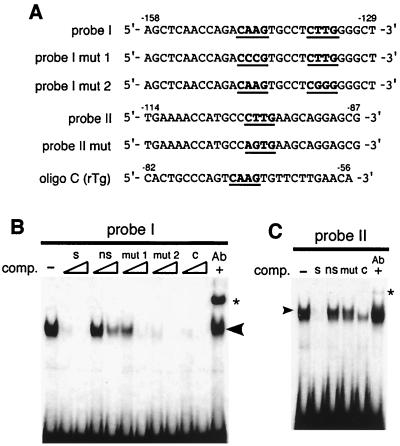
FIG. 7.
The T/EBP/NKX2.1 minimal consensus sequence in the mouse claudin-18a1 gene promoter specifically binds to NCI-H441 nuclear proteins. (A) Sequences of probes and competitors used in electrophoretic gel mobility shift analysis. Oligo C is taken from the rat thyroglobulin promoter (rTG) (−82 to −56 bp), which had been identified as a T/EBP/NKX2.1 binding site (7). Putative T/EBP/NKX2.1 consensus sequences (19) are shown in boldface and underlined. (B and C) Electrophoretic mobility shift assay of the T/EBP/NKX2.1 binding site. NCI-H441 nuclear extracts were incubated with 32P-labeled probe I (B) or probe II (C). The specifically retarded complex is shown by an arrowhead. Competition assays were performed with 100-fold (C) or 100- and 500-fold (B) excesses of unlabeled specific (lanes s), nonspecific (lanes ns), mutated (lanes mut 1 and mut 2), or oligo C (lanes c) oligonucleotides. For antibody supershift analysis, TTF1-specific monoclonal antibody was added to the reaction mixture (lanes Ab +). Asterisks indicate the position of the supershifted complex.