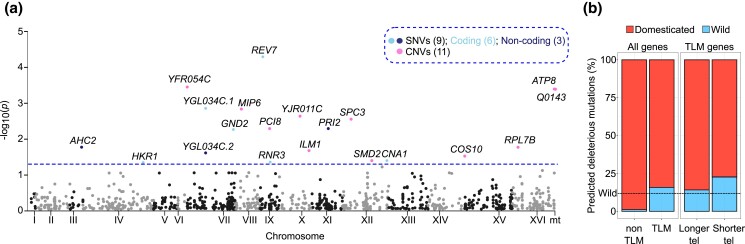
Fig. 4.
TL genetic variants. a) Manhattan plot showing the position of the GWAS variants across the genome. 20 variants are beyond the genome-wide significance threshold (P < 0.05, dashed line). SNVs: single nucleotide variants; CNVs: copy number variants. Numbers in brackets denote the number of variants contained in that group. For simplicity, only the first 1,000 tested variants are shown in the plot. b) Fraction of TLM and non-TLM genes carrying predicted loss-of-function mutations in euploid diploid domesticated (n = 350) and wild (n = 49) isolates (total n = 399). Isolates classified as unassigned (n = 156) were not considered in this analysis. TLM genes are further subdivided into the ones conferring shorter vs longer telomeres when deleted. The dashed line indicates the fraction of wild strains in the 399 S. cerevisiae collection (12%).